Imagine walking into a factory where autonomous machines glide silently between workstations, robotic arms precisely transfer heavy components without human intervention, and intelligent systems predictively manage inventory before shortages occur. This isn't science fiction – it's today's reality powered by Material Handling Robots. As warehouse labor shortages reach critical levels and global supply chains demand unprecedented flexibility, manufacturers and logistics providers are turning to five revolutionary robotic solutions. This article reveals how these transformative technologies are fundamentally reshaping material handling operations while providing unexpected benefits that extend far beyond mere automation.
The AI-Driven Evolution of Material Handling Robots
The transition from rigid conveyors to intelligent robotic systems represents more than just technological progress – it's a fundamental paradigm shift in how materials move through facilities. What started in the 1960s with fixed-sequence machines has evolved into cognitive systems using LiDAR sensors, machine learning algorithms, and real-time AI processing. These robots no longer merely respond to pre-programmed commands but adapt to environmental changes, predict workflow bottlenecks, and collaborate with human workers in shared spaces. The key driver? The integration of artificial intelligence has transformed Material Handling Robots from automated tools into predictive problem-solvers that continuously optimize material flow.
5 Revolutionary Types of Material Handling Robots Explained
Each category offers distinct solutions to material flow challenges:
1. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) - The Flexible Navigators
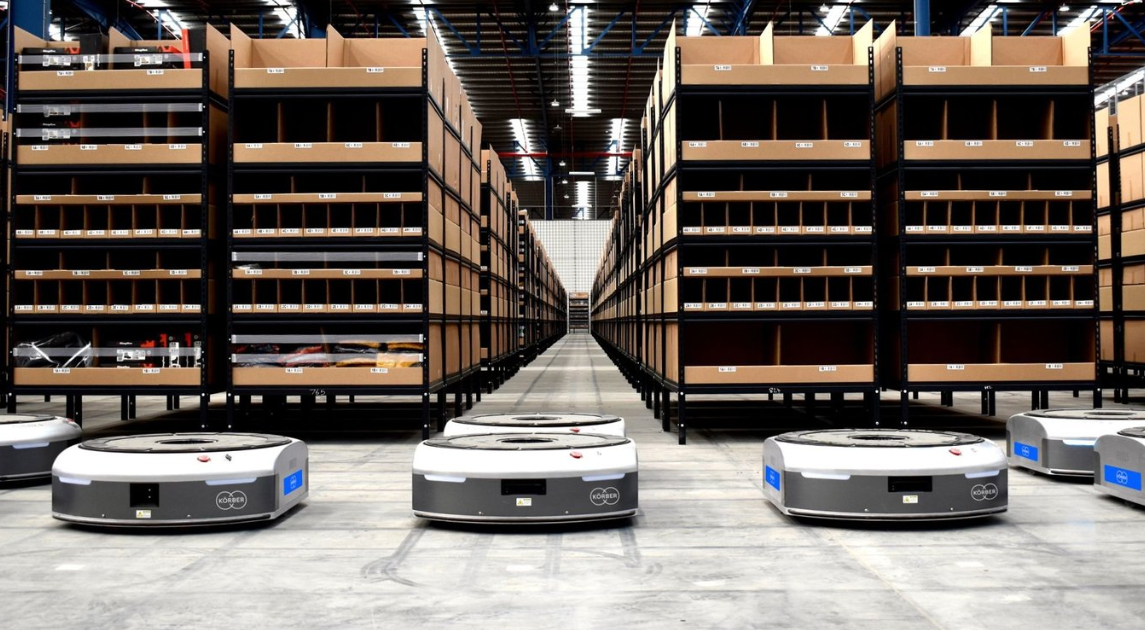

Unlike traditional AGVs that require physical guides, AMRs create dynamic digital maps using simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) technology. Their sophisticated sensors detect obstacles in real-time while prioritizing mission-critical tasks through AI-powered fleet management systems. The latest innovation? Swarm intelligence enables coordinated group behaviors where AMRs collaboratively solve traffic flow problems without central oversight. These adaptive systems excel in unpredictable environments like e-commerce fulfillment centers where layout changes happen weekly.
Common Applications: Dynamic warehouse replenishment, hospital lab specimen transport, manufacturing work-in-progress movement between cells. AMRs offer flexibility unattainable by conveyor systems at a fraction of traditional automation installation time.
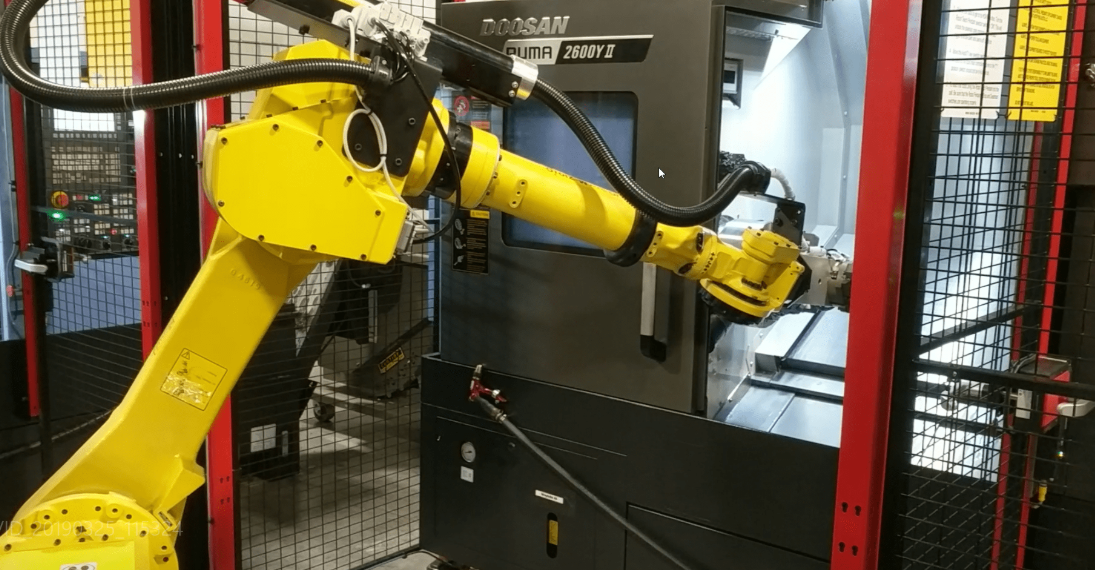
2. Articulated Robotic Arms - The Precision Lifters
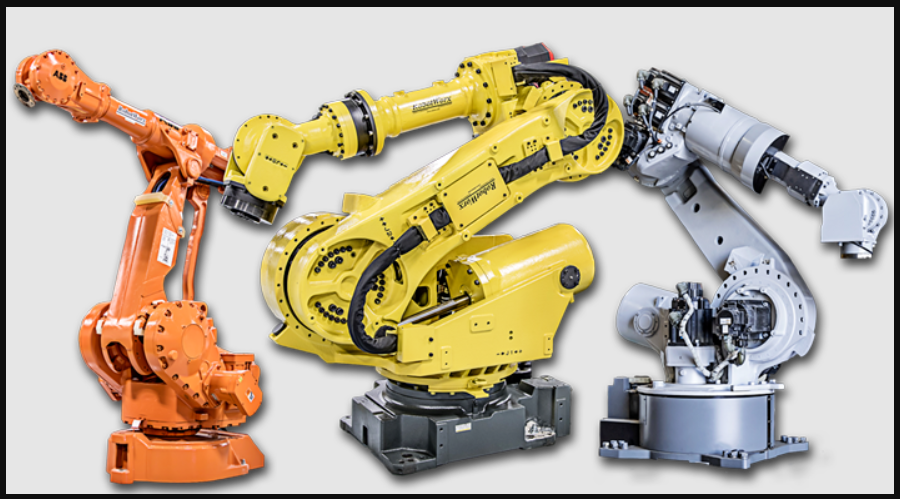

With up to seven axes of rotation mimicking the human arm's dexterity, these articulated robots reach into tight spaces unreachable by conventional equipment. Advanced variants feature enhanced payload capacities exceeding 1,000 kg without compromising positioning accuracy (±0.02mm). The game-changing innovation? Vision-guided picking systems combined with machine learning allow these robots to handle variable objects without pre-programming, making them indispensable for applications like mixed-SKU palletizing and complex machine tending tasks previously requiring skilled human operators.
Common Applications: Automotive assembly lines, precision machine loading/unloading, multi-SKU depalletizing systems in distribution centers. Their reprogrammability provides rapid changeover between product types unlike fixed automation.
3. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) - The Reliable Workhorses

Modern AGVs have transformed beyond simple wire-following machines into sophisticated laser-guided systems with integrated safety features. The latest innovation? Natural feature navigation eliminates infrastructure modifications entirely, saving installation costs while allowing route modifications via software updates. What makes AGVs uniquely reliable? Their infrastructure dependence creates predictable pathing vital for critical applications like pharmaceutical manufacturing where material flow consistency impacts regulatory compliance.
Common Applications: High-volume production line feeding, trailer loading operations, cross-dock transfer stations. Their reliability makes them indispensable in environments where uptime directly impacts throughput rates.
Explore how these systems combat labor challenges: Material Handling Robots: Your Secret Weapon Against Soaring Costs & Labor Shortages
4. Collaborative Robots (Cobots) - The Human Amplifiers
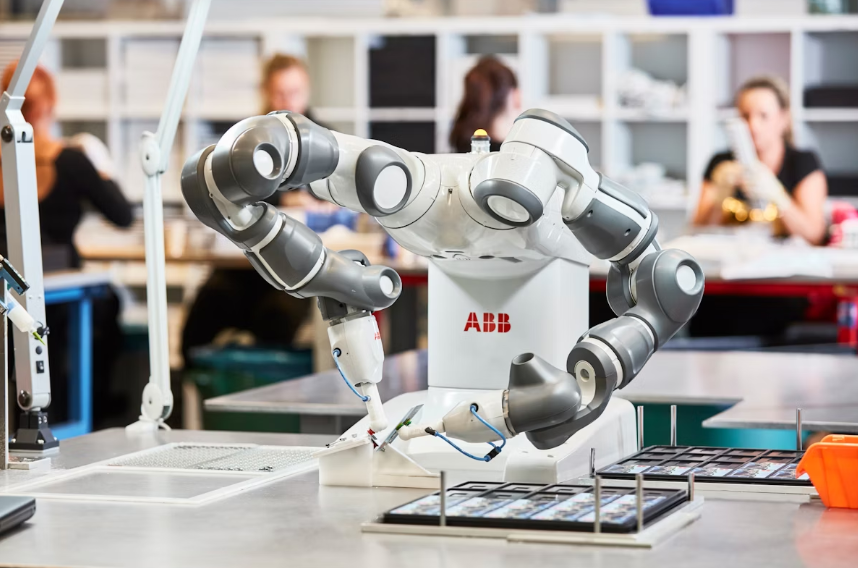

Unlike traditional industrial robots requiring safety cages, cobots feature advanced force-limiting technology and proximity sensors enabling safe interaction with human coworkers. The innovation breakthrough? Adaptive grippers combine with real-time computer vision to enable cobots to handle tasks requiring human-level dexterity. Safety certifications (ISO 10218 and ISO/TS 15066) combined with intuitive programming interfaces allow rapid task redeployment, enabling flexible work cell configurations that were previously unattainable.
Common Applications: Hybrid assembly stations, ergonomic lift-assist applications, precision kitting operations. Their unique combination of flexibility and safety creates operational possibilities beyond mere automation.
5. Automated Storage/Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) - The High-Density Masters
These intelligent cranes operate within automated storage structures reaching heights of over 100 feet with positioning accuracy within millimeters. The revolutionary development? Goods-to-person robotic systems combine vertical storage density with horizontal AMR technology for efficient item retrieval. Modern shuttle systems achieve throughput rates exceeding 1,000 transactions per hour while maintaining 99.99% inventory accuracy through continuous location verification. This unique solution transforms inventory accuracy from periodic audit events to continuous real-time verification.
Common Applications: High-value component warehousing, pharmaceutical distribution centers, e-commerce micro-fulfillment centers. Their storage density and inventory control capabilities provide unmatched ROI in space-constrained environments.
Decoding Material Flow: Comparative Analysis
| Robot Type | Flexibility | Payload Capacity | Infrastructure Requirements | Adaptability to Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomous Mobile Robots | High | Medium (up to 1500kg) | Minimal | Re-maps autonomously |
| Articulated Arms | Medium | High (to 2000kg) | Work cell setup | Requires reprogramming |
| Automated Guided Vehicles | Low | Very High (to 50,000kg) | Navigation infrastructure | Route changes complex |
| Collaborative Robots | Very High | Low (to 35kg) | Minimal | On-the-fly adjustments |
| AS/RS Systems | Low | Medium (to 1000kg) | Storage structure | System expansion possible |
The hidden breakthrough? Most modern facilities now deploy hybrid robotic ecosystems. Picture AMRs transporting components to cobot-assisted assembly stations with AS/RS systems managing raw material inventory – a closed-loop system where robots replenish robots. This layered approach creates unprecedented operational flexibility unavailable with single-technology solutions.
Choosing Optimal Robotic Solutions
Implementing the right Types of Material Handling Robots requires strategic assessment:
Flow Pattern Analysis: Linear material flow suggests AGVs while complex multi-point transfers benefit from AMRs. Articulated arms excel at confined workstations.
Operational Scalability: Autonomous mobile robots provide immediate scalability through fleet additions while AS/RS systems deliver density advantages.
AI Integration Potential: Prioritize systems offering open APIs that allow integration with predictive analytics platforms for demand-based material flow.
Financial Perspective: Consider operational flexibility as tangible financial value. A Yale University study revealed facilities with flexible material handling systems reduced changeover costs by 63% during seasonal demand shifts.
The real transformation occurs when companies use robotic material flow data to predict supply chain disruptions. One automotive supplier achieved 23% inventory reduction through predictive analytics derived from handling robot workflow patterns.
Discover how this revolution transforms industries: Handling Robots: The Silent Revolution Transforming AI and Automation
Future Material Flow: Emerging Technologies
The horizon reveals even more transformative applications:
Magnetic Mobility Systems: Contactless movement through electromagnetic field manipulation enables "floating" material transfer.
Predictive Fleet Management: AI analyzing AMR fleet behavior patterns can forecast future traffic bottlenecks before they occur.
Self-Repairing Systems: Advanced diagnostics predict maintenance needs 30% earlier than conventional methods.
Ambient Intelligence Environments: Warehouse structures with embedded sensors providing contextual awareness to all operating robots.
The common thread? Each innovation increases operational resilience, allowing facilities to dynamically adapt to disruptions rather than merely withstand them.
Industry Insights: Robotic Material Handling FAQs
Q: What distinguishes modern AGVs from Autonomous Mobile Robots?
Modern Automated Guided Vehicles rely on physical infrastructure like magnetic tape or wires for navigation, making their paths predictable but inflexible. Autonomous Mobile Robots dynamically navigate using sophisticated sensors and real-time mapping, continuously creating optimized routes around obstacles. This fundamental technological difference determines their application suitability.
Q: Can existing warehouses integrate these robots without operational disruption?
Implementation strategies matter significantly. Modern robotics companies offer phased rollouts where AMRs or collaborative robots are deployed in specific zones without full facility shutdowns. Case studies demonstrate successful implementation during normal operations using weekend installations and temporary containment structures. The average installation timeframe has decreased by 40% in the last 3 years.
Q: How do ROI calculations differ for distinct robot categories?
Articulated arms typically deliver ROI through precision and throughput increases in confined spaces. AS/RS systems generate dramatic warehouse density savings. AMRs create value through operational flexibility during seasonal peaks. While AGVs achieve cost-per-pound transport reductions at scale, collaborative robots deliver unique value in human-robot workflows. Each requires distinct financial modeling incorporating soft cost savings in labor flexibility and error reduction.
Q: How does artificial intelligence enhance modern material handling robots?
AI transforms robotic systems from automated tools into predictive problem-solvers. Machine learning algorithms analyze handling patterns to optimize warehouse layouts while computer vision enables adaptive object recognition without programming. Most significantly, predictive maintenance algorithms analyze operational data to prevent failures before they impact production. These cognitive capabilities separate modern systems from traditional automation.
Material Handling Transformation Conclusion
Understanding the five core Types of Material Handling Robots reveals more than technical specifications – it unveils a fundamental shift in how facilities operate. AMRs provide unprecedented flexibility where traditional AGVs offer rock-solid reliability. Collaborative robots enhance human capabilities while AS/RS transforms inventory management. Most strategically significant is how these technologies create operational resilience in unpredictable markets. Leading manufacturers now report robotic material handling systems helped them adapt to supply chain disruptions 50% faster than competitors using traditional methods. This operational adaptability represents the most valuable – and least discussed – benefit of the robotic revolution.