From precision surgery to automated diagnostics, Medical Robotics is transforming modern medicine at unprecedented speeds. This technological revolution is enhancing surgical precision beyond human capabilities, accelerating patient recovery times, and democratizing access to specialized care worldwide. As global investments in healthcare robotics surge past $12 billion annually, these intelligent systems are addressing critical challenges like surgeon shortages and procedural variability while opening new frontiers in treatment personalization. The da Vinci Surgical System represents the gold standard in robotic-assisted surgery. This sophisticated platform translates a surgeon's hand movements into smaller, more precise actions through miniaturized instruments. With 3DHD visualization and tremor filtration technology, procedures like prostatectomies now show complication reductions of up to 63%. The system's wristed instruments provide seven degrees of motion – two more than the human hand – enabling unparalleled access to confined anatomical spaces. Exoskeleton systems like EksoNR are helping paralyzed patients regain mobility through computer-controlled support. These wearable Medical Robotics solutions use motion sensors and AI to adapt assistance levels based on real-time biofeedback. Clinical trials demonstrate 72% of stroke patients achieving improved gait patterns after just 8 weeks of robotic therapy. The Lokomat system takes this further with body-weight supported treadmill training, showing 40% greater functional recovery rates than conventional methods. InTelRobotics' RP-VITA provides remote physician presence through autonomous navigation and HD telehealth capabilities. These mobile platforms address critical specialist shortages, particularly in rural regions where 65% of US counties lack practicing surgeons. Equipped with digital stethoscopes and otoscopes, they enable real-time diagnostics during emergency scenarios. Recent FDA clearance now allows their deployment in stroke assessments where timely intervention reduces disability risks by 30%. Robotic dispensers like Swisslog's BoxPicker handle 98% accuracy in medication distribution, reducing human dosing errors that affect 1.3 million Americans annually. These Medical Robotics solutions incorporate barcode verification and inventory tracking while processing over 350 prescriptions hourly. The automated systems can operate 24/7 without fatigue, ensuring continuous medication availability in hospital pharmacies nationwide. Experimental microbots from MIT's research labs demonstrate cancer drug delivery with 90% precision to tumor sites. Magnetic propulsion systems guide these micro-scale robots through vasculature networks, minimizing systemic toxicity through localized treatment. Current prototypes measuring 50-100 microns can navigate through the bloodstream while carrying payloads of therapeutic agents directly to affected tissues. Xenex LightStrike robots deploy pulsed xenon UV technology to eliminate pathogens in under 10 minutes per room. Hospitals implementing these Medical Robotics solutions report 45-70% reductions in MRSA and C.diff infection rates. Their autonomous navigation systems map hospital floors for comprehensive coverage without human supervision. The robots use advanced algorithms to determine optimal disinfection patterns, ensuring complete room sterilization between patient uses. Combining computer vision with robotic precision, systems like Paige Prostate detect cancer indicators with 99.3% sensitivity - outperforming human pathologists. These platforms analyze tissue morphology patterns across millions of data points, identifying biomarkers invisible to conventional microscopy. Ongoing FDA approvals are accelerating implementation across diagnostic pathology labs globally. The integration of machine learning allows these systems to continuously improve their diagnostic accuracy as they process more cases. Next-generation developments focus on haptic feedback systems for robotic surgeons and biodegradable nanobots capable of targeted drug release over weeks. Research in neural-controlled prosthetics promises thought-driven movement restoration, with 65 research teams worldwide pursuing brain-machine interfaces. Regulatory frameworks are evolving rapidly, with the FDA's 2023 Digital Health Innovation Action Plan creating accelerated pathways for AI-enhanced medical devices. Industry analysts predict the global Medical Robotics market will exceed $35 billion by 2028, driven by technological advancements and increasing acceptance among medical professionals. Advanced platforms like da Vinci cost approximately $2 million initially, plus $150,000 annual maintenance. However, studies show they generate $700,000-$1.2 million annual savings through reduced complication rates and shorter hospital stays. Many hospitals implement financing programs that spread the capital costs over several years while realizing immediate clinical benefits. Robotic procedures show 21% fewer overall complications according to JAMA research. The magnification capabilities and tremor elimination particularly benefit delicate operations where millimeter precision matters. The closed surgical environment created by robotic systems also significantly reduces the risk of infection compared to open procedures. Surgeons complete 20-30 supervised procedures plus simulator training averaging 45 hours. Certification requires demonstrated proficiency across 5 key performance metrics measured by the systems' tracking software. Ongoing training is mandatory, with surgeons required to complete annual competency assessments and maintain case volume standards to retain robotic surgery privileges.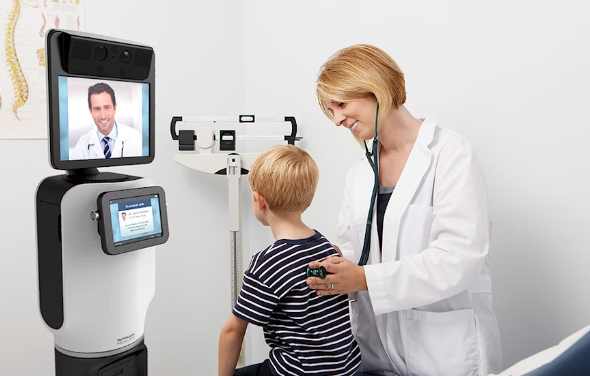
Surgical Robotics: Precision Beyond Human Capability
Rehabilitation Robotics: Restoring Movement Through Technology
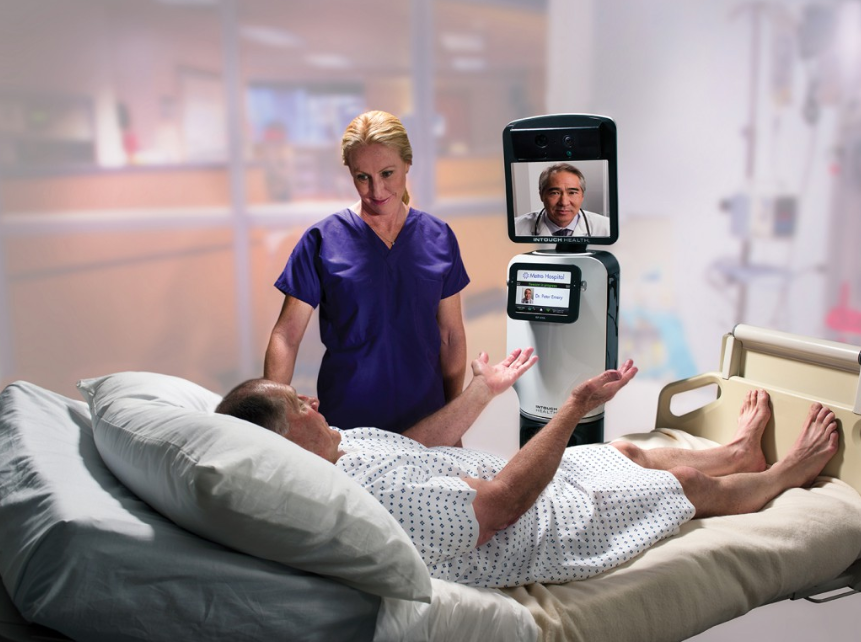
Telepresence Robots: Expanding Specialist Access
Pharmacy Automation Systems
Nanobots in Targeted Therapy
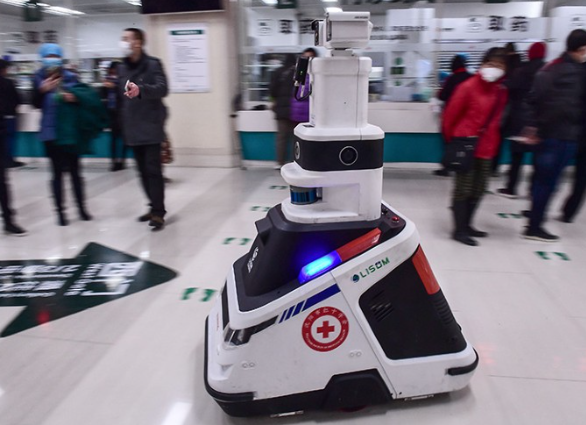
Disinfection Robots: Combating HAIs
AI-Enhanced Diagnostic Robotics
The Future Landscape of Medical Robotics
Frequently Asked Questions
How expensive are surgical robotics systems?
Are robotic surgeries safer than traditional methods?
What training do robotic surgeons require?