Imagine a surgeon operating with superhuman precision through incisions smaller than a dime, controlling robotic arms that eliminate hand tremors while magnifying the surgical field tenfold. This isn't science fiction—it's the daily reality in thousands of operating rooms worldwide, thanks to one groundbreaking technology: the da Vinci Surgical System. As the undisputed leader in Medical Robotics, this mechanical marvel has performed over 10 million procedures since its debut, fundamentally transforming modern surgery.
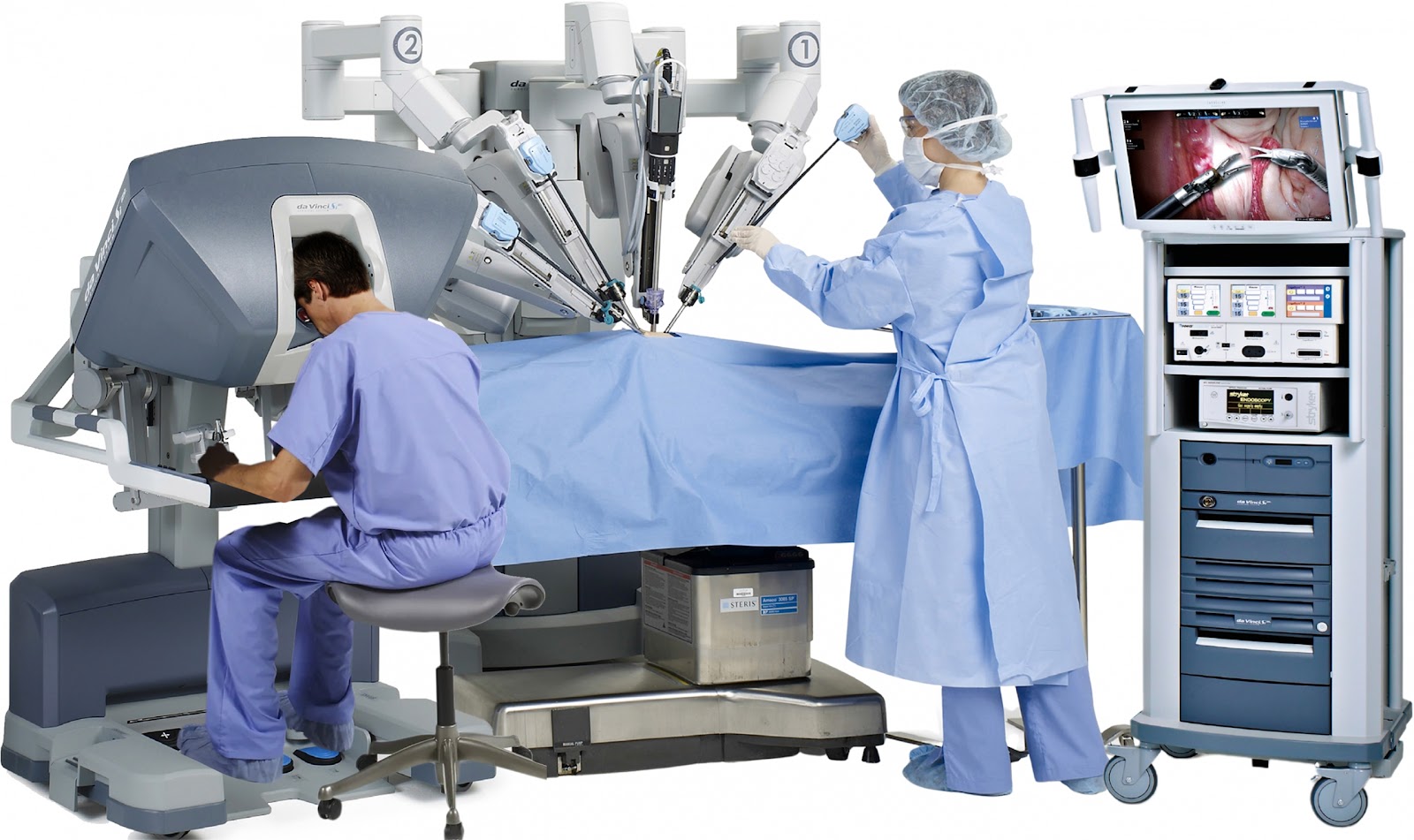
Developed by Intuitive Surgical, the da Vinci system represents the pinnacle of robotic-assisted surgery. Its iconic four-armed silhouette has become synonymous with cutting-edge Medical Robots, combining advanced engineering with surgical expertise to achieve outcomes previously deemed impossible. The system allows surgeons to perform complex procedures through minimal incisions with 3D high-definition visualization and wristed instruments that bend and rotate far beyond the natural range of human hands.
Discover Cutting-Edge AI InnovationsAnatomy of a Surgical Revolution: What Makes da Vinci Unique
The Visionary Behind the Robot
The da Vinci system originated from Pentagon-funded research in the 1980s aimed at developing telesurgery solutions for battlefield medicine. Stanford Research Institute engineers pioneered the foundational technology, which Intuitive Surgical later commercialized. The system received FDA clearance in 2000, initially for laparoscopic procedures, before expanding to cardiac, thoracic, urologic, and gynecologic surgeries.
Quadruple-Arm Precision Engineering
At the heart of da Vinci's capabilities are its four interactive robotic arms:
The surgeon console: Where the surgeon sits comfortably with immersive 3D vision and intuitive controls
Patient-side cart: Positions above the patient with interchangeable EndoWrist instruments
Vision cart: Provides core processing power and enhanced visualization systems
Wristed instruments: Feature seven degrees of freedom (vs. four in human wrists)
90%
Reduction in physician fatigue compared to manual laparoscopy
10x Magnification
3D HD visualization surpassing human eyesight
67%
Decrease in postoperative complications in prostatectomies
Miracles in the Operating Room: What da Vinci Medical Robots Can Achieve
Precision Beyond Human Limits
These surgical systems have revolutionized delicate procedures where millimeter-level accuracy determines outcomes:
Prostatectomies: Reduced nerve damage preserves urinary continence (92% vs. 75% in open surgery) and sexual function
Cardiac valve repair: Enables beating-heart repairs impossible with traditional methods
Microsurgical anastomoses: Robotic suturing of vessels under 1mm diameter
Single-site cholecystectomies: Gallbladder removal through a single 2.5cm incision
The New Surgical Paradigm: Robotic Advantages
| Parameter | Open Surgery | Traditional Laparoscopy | Robotic Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incision Size | 15-30 cm | 3-5 ports (5-12mm each) | 1-2 cm (single site) |
| Recovery Time | 4-8 weeks | 2-4 weeks | 1-2 weeks |
| Blood Loss | High (300-1000ml) | Medium (150-500ml) | Low (20-100ml) |
| Surgical Precision | ?????? | ???????? | ?????????? |
Why da Vinci Reigns Supreme: The Dominance of Surgical Medical Robots
Clinical Validation
With over 6,000 peer-reviewed publications demonstrating superior outcomes across specialties, da Vinci maintains an evidence-based advantage:
Urology: 86% cancer control rates at 10 years (vs 78% open)
Colorectal: 52% reduction in surgical site infections
Gynecology: 60% faster return to normal activities
The Ecosystem Advantage
da Vinci's success stems from its integrated ecosystem: 5,600 installed systems worldwide, trained surgeon network exceeding 55,000 professionals, and continuous innovation cycles (average 18-month hardware upgrades). Unlike single-purpose competitors, da Vinci's modular platform adapts to diverse surgical specialties through instrument swaps rather than system replacements.
The Da Vinci Effect: How Robotic Surgery Changed Healthcare Economics
The system's high initial cost ($0.5-$2.5 million per unit) is offset by shorter hospital stays (average 1.6 days vs 4.9 for open surgery), reduced complications ($20,000 savings per avoided adverse event), and premium reimbursement structures. Hospitals report 23% higher surgical volumes and 17% increased market share after robotic implementation.
Next-Generation Medical Robots: Beyond da Vinci
Emerging Challengers
Medtronic Hugo RAS: Modular system using commodity hardware components
CMR Versius: Portable system with modular arm cart
Johnson & Johnson Ottava: Space-saving design with integrated operating table
The AI Frontier
Next-gen platforms incorporate machine learning algorithms for predictive tissue analytics, autonomous suturing, and virtual safety barriers. Prototype systems show promise in real-time surgical guidance:
Augmented reality overlays identifying critical structures
Adaptive tremor filtration adjusting to surgeon fatigue levels
Force feedback replicating tissue resistance (absent in current systems)
Essential Questions About Medical Robots
Q: How long does da Vinci certification take?
A: Surgeons undergo 3-6 months of intensive training including simulation modules, procedural observerships, and proctored operations. Initial certification requires 20 supervised cases with quarterly competency reviews.
Q: Can robotic surgery replace surgeons?
A: Absolutely not. These systems lack autonomous decision-making capabilities. Robotic platforms function as advanced tools under complete surgeon control with no AI autonomy. Human judgment remains irreplaceable for intraoperative decisions.
Q: What are the main barriers to wider adoption?
A: Despite decreasing costs, capital expenditure remains significant. Newer challenges include procedure-specific reimbursement coding and specialized facility requirements. Emerging markets face infrastructure limitations including stable power supply and broadband connectivity needs.