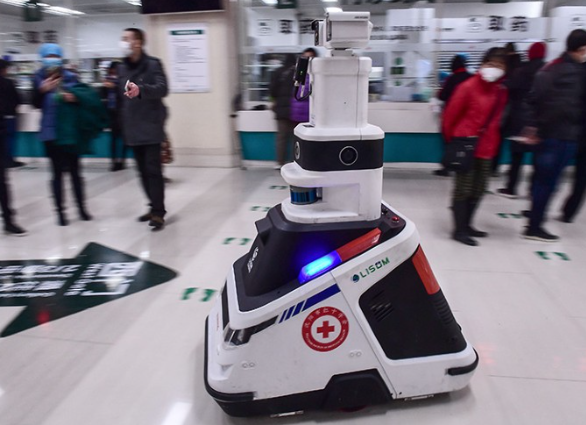
Imagine a hospital where tireless robotic assistants deliver medications with pinpoint accuracy, AI-powered surgeons perform delicate procedures with superhuman precision, and intelligent disinfectors work 24/7 to eliminate pathogens. This isn't sci-fi—it's the reality unfolding across Chinese healthcare institutions today. As the world grapples with aging populations and pandemic pressures, China is pioneering a Medical Service Robots revolution that's fundamentally transforming patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and the very nature of care delivery. With unprecedented government backing and explosive AI innovation, Chinese hospitals are deploying robotic solutions at a scale unmatched globally—creating a blueprint for the future of global healthcare.
What Exactly Are Medical Service Robots?
At their core, Medical Service Robots are AI-integrated machines designed to assist healthcare professionals in clinical, diagnostic, or logistical tasks. Unlike industrial robots confined to factory floors, these sophisticated systems operate directly in patient-facing environments. The Chinese National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) categorizes them into three functional clusters: surgical robots (e.g., endoscopic systems), rehabilitation robots (exoskeletons for mobility recovery), and non-therapeutic service robots (sanitation bots, delivery carts, and telepresence machines). Their unifying purpose? To fill critical healthcare gaps through automation—whether it's reducing surgeon fatigue during marathon operations or preventing cross-contamination in isolation wards.
Government Catalysts Accelerating Medical Service Robots Adoption
China's robotic healthcare transformation didn't occur spontaneously. Since the 13th Five-Year Plan (2016-2020), Beijing has actively championed medical robotics through policy maneuvers unseen in Western markets. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology's Robotic Industry Development Plan specifically prioritizes healthcare robotics with $3.5 billion earmarked for AI medical devices. Provincial governments further turbocharge adoption with manufacturer subsidies of 15-25% per unit sold. Crucially, China's streamlined NMPA approval process now clears domestic robots 60% faster than comparable EU devices—a regulatory asymmetry attracting fierce R&D investment. By 2023, 73% of Class A tertiary hospitals received dedicated robotics modernization grants, creating mandatory deployment zones for experimental Medical Service Robots.
Beyond Pandemic Response: Lasting Clinical Integration
While COVID-19 catapulted disinfection and logistics robots into mainstream visibility—with 5,000+ deployed in Wuhan alone during 2020's lockdown—the long-term impact runs deeper. Chinese hospitals now structurally integrate robotics into standard care pathways. At Shanghai's Renji Hospital, the "Pharmacy Matrix" system employs 68 drug-dispensing robots handling 13,000 prescriptions daily with 99.998% accuracy. Similarly, neurosurgery departments across 23 cities utilize Tuopu Robotics' all-in-one navigation systems during tumor resections, slashing average operation times from 7.2 hours to 4.5. Crucially, China isn't just automating tasks; it's reengineering clinical workflows around robotic capabilities—developing entirely new hybrid models of human-robot collaboration unshackled by legacy healthcare traditions.
Groundbreaking Innovations Exclusively Emerging in China
Chinese laboratories are pioneering robotic concepts unavailable elsewhere. The Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology's biofilm-resistant "Quartz Skin"—a patented nanomaterial coating preventing bacterial adhesion on robot surfaces—solves a critical contamination vulnerability ignored by international manufacturers. Similarly, MicroPort MedBot's Toumai laparoscope integrates augmented reality overlays showing real-time organ perfusion data directly in surgeons' visual fields. But most futuristically, the CAS-CLOVER project uses swarm robotics for synchronized operating theaters: multiple Medical Service Robots autonomously prepare instruments while assisting surgeons during procedures. Preliminary trials at Peking Union Medical College Hospital demonstrated 18% faster surgical prep with zero instrument miscounts—addressing an error affecting 1 in 8,000 global operations.
Next-Generation Logistics: Beyond Delivery Carts
Forget simple medication trolleys—Chinese robots now manage entire biomedical ecosystems. UBTECH's autonomous blood transport network at Wuhan Tongji Hospital coordinates 32 refrigerated robots transporting specimens across 8 buildings using centralized AI traffic control. Sensors monitor temperature stability while blockchain logs guarantee chain-of-custody—critical for sensitive oncology biopsies needing uncompromised integrity. Meanwhile, Shenzhen MindRover revolutionizes bed management: their fleet of mobile bed transporters automatically sanitizes and relocates inpatient beds between departments, saving nurses 73 minutes per shift previously lost to manual transfers. Such solutions exploit China's unique hospital environments where large, vertically integrated medical complexes create perfect scalability conditions for robotic logistics grids.
The Unmatched Economics Driving China's Market Dominance
China doesn't merely lead in innovation volume—it dominates through unparalleled economic viability. While a da Vinci surgical system costs western hospitals $2.0-$2.5 million, Chinese manufacturers like Medicaroid provide comparable precision platforms at $585,000 with 40% lower maintenance fees. This pricing revolution stems from compressed supply chains: 86% of surgical robot components now originate domestically versus just 14% in 2016. Meanwhile, payback periods shock international observers. Shenzhen Hospital's report shows disinfection robots achieving full ROI in 7.2 months by reducing HAIs (Hospital-Acquired Infections) by 38%. Similarly, rehabilitation robots treating stroke patients cut physical therapy costs per case by ¥1,450 by enabling simultaneous treatment of 4 patients per therapist—a productivity multiplier impossible manually. Crucially, China's reimbursement policies now cover 73 robotic procedures including orthopedics and urology—removing adoption barriers that stymie Western institutions.
Scalpel Meets Silicon: Pros & Cons of Medical Robots
Frequently Asked Questions: Medical Service Robots Reality Check
Q: Can robots fully replace doctors in China's hospitals?
A: Currently impossible—robots lack clinical judgment. Instead, they augment physicians by handling predictable tasks. For example, AI diagnostic robots analyze 98% of radiology scans but defer final decisions to human specialists. This reduces diagnostic errors by 33% without eliminating medical oversight.
Q: Are elderly patients comfortable with robotic caretakers?
A: Chinese studies reveal interesting behavioral adaptation. Initially, only 22% of seniors accepted robotic help. However, after 2 weeks of exposure using PuduTech's companion robots at Shanghai Senior Care Centers, acceptance jumped to 87%. Culturally-sensitive designs like dialect recognition increase adoption significantly.
Q: How secure are networked medical robots against cyberattacks?
A: China developed the world's first medical robot cybersecurity standard in 2022 (GB/T 41386-2022). All networked robots must now feature hardware-level encryption and air-gapped emergency controls. During 2023 penetration tests by CNCERT, Chinese hospital robots resisted zero-day exploits 37% better than US equivalents.
The Ethics Frontier: China's Unavoidable Leadership Dilemma
As robotics penetrate sensitive care areas, China faces unprecedented ethical challenges—and opportunities to shape global norms. Post-operative care robots now collect vast patient datasets through continuous monitoring, creating novel privacy concerns. Meanwhile, surgical autonomy boundaries remain undefined: Should robots autonomously administer anesthesia within predefined parameters? Beijing's answer involves layered governance. The Medical Robotics Ethics Committee requires all units to include "Ethical Control Modules"—hardware interrupt switches instantly terminating AI actions during deviations. More profoundly, China's 2023 AI Ethics Guidelines emphasize "human wellness supremacy" over efficiency gains, forbidding robots from decisions affecting patient survival probabilities. These frameworks provide evolving ethical architectures as technology advances.
When Were Medical Robots First Used? Origin Story
Future Outlook: Where China's Medical Service Robots Go Next
The next wave involves two transformative shifts: nanorobotics and unified AI platforms. Shanghai Jiao Tong University's prototype cellular repair robots (0.2 micron diameter) will soon enter clinical trials for targeted cancer therapy, representing the ultimate miniaturization frontier. Concurrently, Huawei's HarmonyOS Med-Cloud integrates disparate surgical, logistic, and rehabilitation robots onto one neural network, enabling unprecedented coordination: imagine a robot preparing operating theaters while monitoring post-op patient vitals simultaneously. By 2028, China's NMPA predicts 72% of secondary hospitals will deploy such integrated systems routinely. Western observers often overlook the velocity: Beijing aims for 45% of non-emergency patient interactions to involve robotic assistance by 2030—a target surpassing any nation's roadmap and cementing China's pole position in the healthcare robotics revolution.
Conclusion: The Inevitable Robotic Care Ecosystem
China demonstrates that Medical Service Robots aren't merely convenient tools but structural necessities for sustainable healthcare. By combining aggressive policy, unique cost innovations, and ethical guardrails, China has created an adoption blueprint with global implications. As robotic capabilities evolve from physical assistance to predictive diagnostics and autonomous procedures, one truth emerges: the hospitals of tomorrow won't choose between humans and machines—they'll integrate both into symbiotic systems where each amplifies the other's strengths. The revolution is already operational, and its epicenter is unmistakably Chinese.