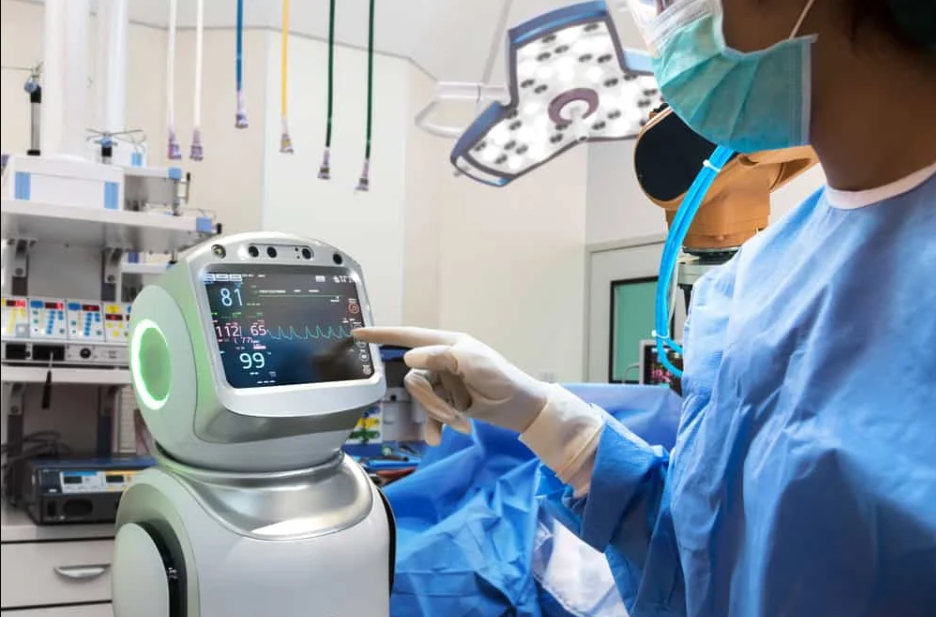
Imagine a surgical assistant with tremor-free hands that can operate through an incision smaller than a dime, or a tireless caregiver that never loses patience during rehabilitation. Medical robots are not science fiction - they're actively transforming hospitals and clinics worldwide. In this eye-opening exploration, we unveil the revolutionary impact of robotics in medicine through Facts About Medical Robots that prove we're living in the future of healthcare.
What Exactly Are Medical Robots?
Medical robots encompass specialized robotic systems designed for healthcare applications, ranging from surgical assistance and rehabilitation therapy to telepresence and hospital logistics. These sophisticated machines combine precision engineering with advanced AI to perform tasks with superhuman accuracy. Unlike industrial robots, medical variants operate in highly sensitive environments alongside vulnerable patients, requiring exceptional safety protocols and intuitive interfaces. The category includes systems for direct patient interaction like surgical arms as well as backend support robots handling medication dispensing and sterilization.
Fact 1: Surgical Robots Enable Superhuman Precision Unattainable by Humans
The most celebrated Facts About Medical Robots concern their surgical capabilities. The da Vinci system, for instance, filters out surgeon hand tremors completely while scaling movements down to 1:5 ratios. This means when a surgeon moves their hand 1 inch, the robotic instrument moves just 0.2 inches inside the patient. This micro-precision enables procedures impossible with traditional methods - especially critical in microsurgeries like nerve reconstruction where instruments operate at sub-millimeter scales. Robotic joint replacements show 43% better alignment accuracy versus manual techniques according to recent Journal of Orthopaedic Research data.
Fact 2: Robots Have Performed Over 10 Million Surgeries Globally
Cumulative robotic surgery counts recently passed the ten million milestone worldwide. What began with the first documented robotic surgery in 1985 (a neurosurgical biopsy using PUMA 560) has exploded into mainstream practice. Cardiovascular procedures lead adoption (31%), followed by urology (28%) and gynecology (24%) according to MedTech Dive's 2024 analysis. This massive dataset validates safety profiles: robotic gallbladder removals show 30% fewer complications than laparoscopic approaches, while prostate surgeries have reduced positive margin rates (cancer left behind) from 35% to 15% versus open surgery.
Fact 3: They're Transforming Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Beyond the operating room, exoskeletons and therapeutic robots help patients relearn movement after neurological injuries. Devices like EksoNR allow paralyzed patients to walk during therapy by providing precisely calibrated weight support and gait guidance. The game-changing aspect? These robots collect 2,000 data points per session - measuring joint angles, weight distribution, and muscle activation far beyond human observation capacity. Columbia University research shows patients using robotic gait trainers achieve walking independence 40% faster than conventional therapy alone.
For stroke victims, robotic arms like InMotion provide intensive, repeatable therapy that maintains perfect form through thousands of movements. This "massed practice" approach triggers neuroplasticity more effectively than human therapists can physically deliver. The clinical impact is quantifiable: studies reveal 70% greater recovery in arm function versus traditional methods when patients start robotic therapy within three months post-stroke, with benefits persisting five years later.
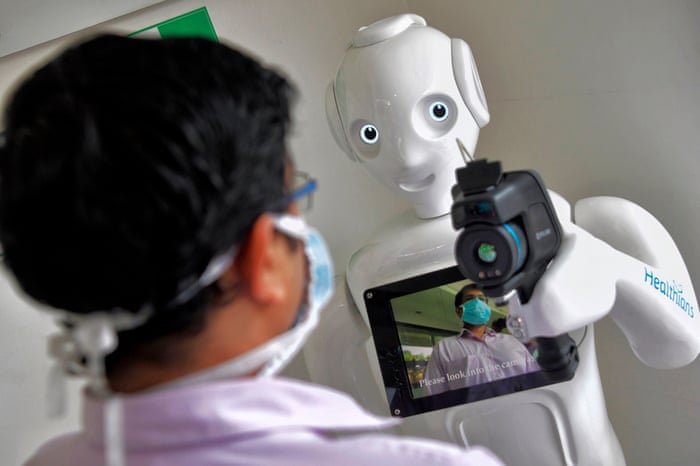
Fact 4: Disinfection Robots Eliminate 99.99% of Hospital Pathogens
Invisible killers lurk on hospital surfaces - CDC data shows healthcare-associated infections affect 1 in 31 patients daily. Enter ultraviolet disinfection robots like the Xenex LightStrike, which blasts pathogens with intense pulsed UV light. These autonomous units cover entire rooms in 10-15 minutes, destroying viruses, bacteria and spores by shredding their DNA at molecular level. University of Texas MD Anderson research demonstrates UV robots reduce C. difficile infections by 63% and MRSA by 45% in treated areas. When combined with hydrogen peroxide vapor bots, some hospitals report 87% lower infection transmission rates.
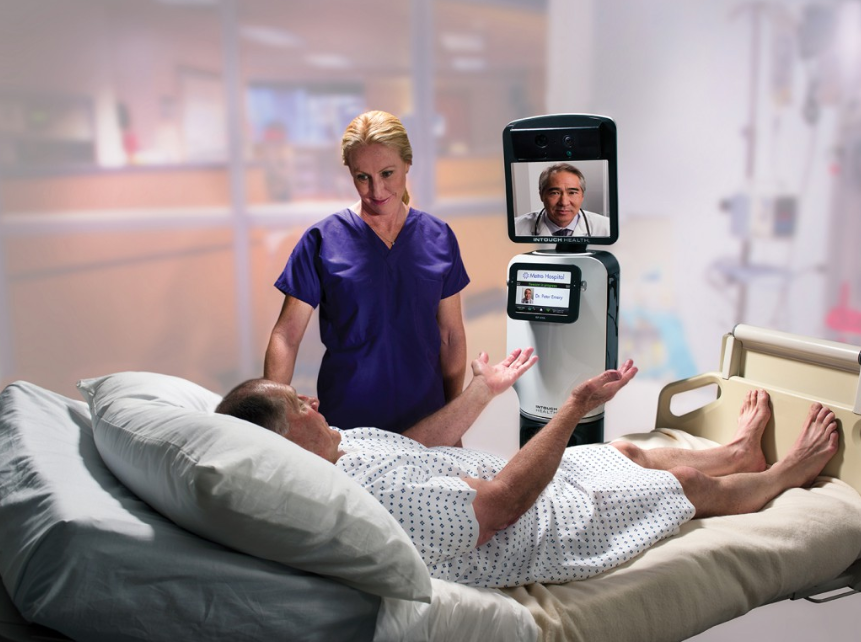
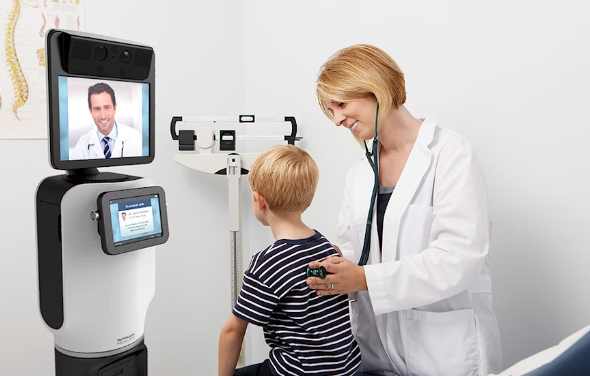
Fact 5: Telepresence Robots Grant 24/7 Specialist Access
Rural communities and underserved areas gain specialist access through robotic avatars with HD screens, cameras, and mobility systems controlled remotely by physicians. Doctors "beam in" to emergency rooms from thousands of miles away, directing local staff through procedures. Stanford's telepresence program connects stroke specialists to 23 rural hospitals, cutting "door-to-needle" time for clot-busting drugs from 76 to 44 minutes - crucial for saving brain tissue. What makes these systems revolutionary? The physician can pan, tilt, and zoom cameras to read bedside monitors, examine pupils, or view incisions with magnification impossible in standard telemedicine.
The Medical Robotics Revolution: How da Vinci Became the World's Most Famous Surgical Assistant
The da Vinci system deserves deep examination as the first FDA-approved robotic surgical platform that reached widespread adoption. Its success stems from three innovations: wristed instruments with 540-degree rotation (beating human dexterity), 3DHD visualization with 10x magnification, and intuitive controls that translate surgeon movements into precise robotic actions. While now synonymous with robotic surgery, newer competitors like Versius offer modular portability. However, da Vinci's installed base exceeds 7,500 units worldwide performing 1.2 million procedures annually.
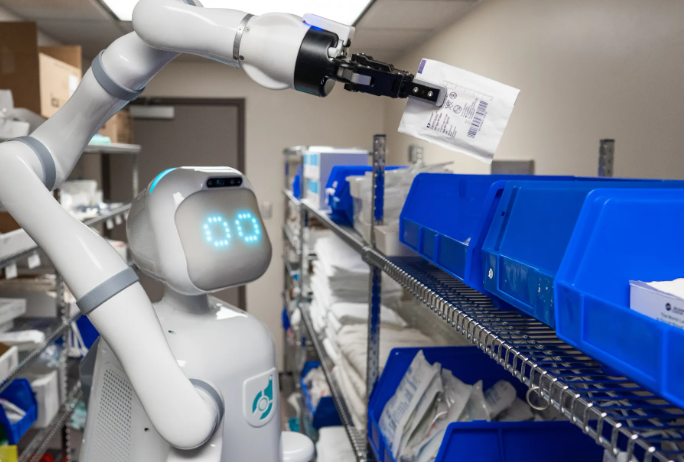
Fact 6: Pharmacy Robots Dispense With 100% Accuracy
Automated pharmacy systems like ScriptPro eliminate deadly medication errors. These robotic pharmacies store, dispense, and label prescriptions with barcode verification at every step. A major California hospital network reported medication errors dropped from 8.3 to 0.5 per 10,000 doses after implementation. The machines prepare IV chemotherapy with 10,000x more precision than humans, mixing milligram-level cytotoxic drugs under sterile hoods. At Massachusetts General, robots handle 5,800 daily medication doses - freeing pharmacists for direct patient care while ensuring perfect dosage accuracy.
Fact 7: Robotic Microsurgeons Are Navigating Your Blood Vessels
Nanorobots represent medicine's final frontier - machines smaller than blood cells navigating vessels to deliver drugs or clear blockages. German scientists recently tested microbots that swim against blood flow using magnetic propulsion, targeting clot sites in animal studies. At ETH Zurich, origami-style microbots unfold inside arteries to remove plaque. While not yet FDA-approved, these prototypes demonstrate capabilities impossible with traditional methods. Industry analysts project nanorobot trials for drug delivery and microsurgery will begin within five years.
Fact 8: AI Makes Surgical Robots Autonomous (Under Supervision)
Modern Facts About Medical Robots must include their evolving intelligence. Systems like Johnson & Johnson's Ottava feature embedded AI that recognizes tissue types using hyperspectral imaging and provides haptic feedback when approaching critical structures. Autonomous functions already exist: Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot (STAR) outperformed human surgeons in intestinal anastomosis trials, making independent stitching decisions while adjusting to tissue movement. The FDA recently cleared the first autonomous spine surgery robot, enabling screw placement with 0.2mm precision without surgeon manipulation.
Fact 9: They Reduce Surgeon Fatigue During Marathon Surgeries
A critical yet underreported benefit: robotic assistance combats surgeon fatigue. Traditional procedures requiring static positions cause muscle fatigue and tremor within 30 minutes. Robotic surgeons operate seated comfortably, with ergonomic controls eliminating physical strain. University of Pittsburgh research measured neuromuscular activation during complex surgeries: console surgeons showed 50-70% lower trapezius and deltoid activity versus manual laparoscopy. This translates to better performance during critical phases of long operations - tremor amplitude increases 300% in surgeons after four manual hours versus consistent robotic precision.
Fact 10: Rehabilitation Robots Read Your Mind (Literally)
The newest rehabilitation bots interpret brain signals to create responsive therapy environments. Patients wearing EEG caps practice moving paralyzed limbs with robotic assistance that activates precisely when brain signals attempt movement. Swiss studies demonstrate this closed-loop system boosts neural pathway formation by 240% compared to passive movement. Similarly, thought-controlled exoskeletons interpret motor cortex signals through non-invasive caps, enabling quadriplegics to feed themselves. As brain-computer interfaces advance, future Facts About Medical Robots will include full neural integration.
Ethical Frontiers: Where Robotics Pushes Healthcare Boundaries
Medical robots raise profound questions about responsibility, economics, and human roles. When autonomous systems outperform surgeons in specific tasks, who assumes liability for errors? Cost presents another hurdle: surgical robots average $2 million per unit plus $3,000 disposable costs per case. This creates healthcare disparity unless coverage policies evolve. Human expertise remains irreplaceable for unexpected complications - the 2024 Brussels Consensus concluded AI-assisted rather than autonomous operations should remain standard for complex cases. We must balance innovation with ethical frameworks ensuring equitable access while prioritizing patient safety.
Robotics in Global Health: Democratizing Advanced Care
Emerging solutions are making robotics accessible globally. Portable systems like Canada's IGARTS weigh under 50 pounds for easy transport to remote areas. India's SS Innovations develops surgical robots at 25% of traditional costs. For physical therapy, Rehab robotics has proven highly effective in low-resource settings: gait trainers reduce the required number of therapists per patient, increasing treatment capacity fivefold in areas with practitioner shortages. These innovations signal a shift from exclusive technology to global care enhancement.
Learn More About Leading AI Innovations
FAQs: Uncovering More Facts About Medical Robots
Q: Are surgical robots performing operations autonomously?
A: Current systems remain tools under direct surgeon control, though AI-assisted autonomy is emerging for specific tasks like suturing under strict supervision. Full autonomy in complex surgeries remains decades away.
Q: How do rehabilitation robots adapt to patient progress?
A: Advanced systems use AI algorithms to analyze performance data, automatically adjusting resistance levels and support parameters while providing therapists with detailed progress metrics showing specific muscle group improvements.
Q: Can telepresence robots replace in-person doctor visits?
A: They excel at consultations, follow-ups, and specialist oversight but cannot perform physical exams. Hybrid models where robots enable frequent remote monitoring with periodic in-person visits show exceptional outcomes in chronic care.
Q: What safeguards prevent robotic medication dispensing errors?
A: Multi-layer verification systems use barcodes, weight measurement of dispensed pills, and photographic confirmation to create error-proof dispensing processes with digital audit trails for every medication prepared.
Envisioning the Robotic Healthcare Landscape of 2035
When we revisit Facts About Medical Robots in the coming decade, expect four transformations: first, miniaturization will enable microscopic bots performing cellular-level repairs; second, swarm robotics will coordinate multiple specialized units during surgeries; third, neural interfaces will allow intuitive control of exoskeletons and prosthetics; finally, cross-platform AI will create seamless integration between robotic surgeons, diagnostic systems, and rehabilitation networks. We stand at the threshold where human expertise merges with machine precision to create unprecedented healing possibilities.