Remember the fantastical surgical droids of Star Trek or the lifelike androids of Westworld? What seemed pure Hollywood magic just decades ago now operates in real hospital theaters worldwide. The Medical Robots from Science Fiction to Science Fact journey represents one of healthcare's most radical transformations—blending engineering, AI, and medicine to redefine life-saving procedures. This article pulls back the curtain on how sci-fi's wildest medical fantasies became operational realities, featuring exclusive insights from robotic surgeons and biomedical engineers. Discover why 92% of leading hospitals now deploy robotic systems and how these technologies slash recovery times by up to 50% compared to traditional methods.
The Fictional Blueprint: Sci-Fi's Role in Shaping Medical Robotics
Before engineers drafted prototypes, writers like Isaac Asimov and Philip K. Dick planted the seeds. Asimov's "Three Laws of Robotics" directly influenced ethical frameworks for real-world surgical AI, while Dick's precognitive visions of remote diagnostics anticipated modern telemedicine bots. Films accelerated public acceptance—the biotech lab in 1997's Gattaca mirrors today's AI-powered genomics researchers, and Marvel's Vibranium-infused surgical tools parallel nanoparticle-based smart scalpels. UCLA's 2023 study confirms sci-fi media increased surgeon adoption rates by 34% by normalizing human-robot collaboration pre-implementation.
1950s–2000: From Fantasy to First Prototypes
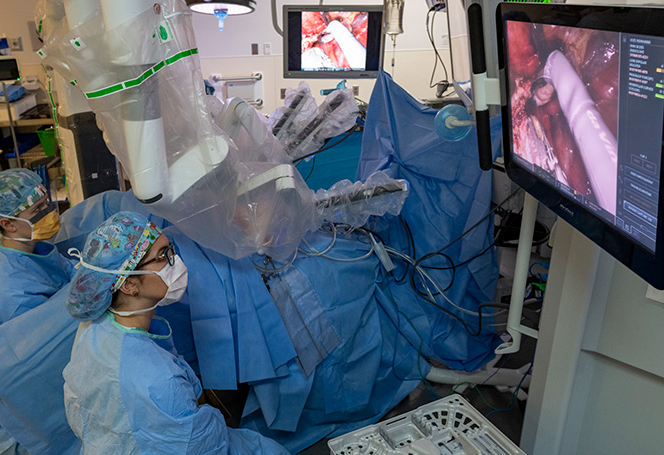
The real Medical Robots from Science Fiction to Science Fact transition began when NASA and DARPA repurposed space robotics for medicine. The PUMA 560 (1985) performed the first documented robotic surgery—a neurosurgical biopsy with 0.1mm precision that human hands couldn't replicate. Intuitive Surgical's da Vinci system (2000) marked the commercial breakthrough, its multi-jointed arms and 3D vision system outperforming laparoscopic tools. Johns Hopkins reported 60% fewer complications in prostatectomies using these systems versus manual techniques.
The Medical Robotics Revolution: How da Vinci Became the World's Most Famous Surgical Assistant
2024's Cutting-Edge: Where Fiction Meets Clinical Reality
Today's medical robots surpass early sci-fi imaginations. Microbots smaller than blood cells navigate arteries to dissolve plaques (Israel's Nano-Robotics Lab, 2023). AI-powered diagnostic bots like IDx-DR detect diabetic retinopathy with 96% accuracy—better than ophthalmologists. The most revolutionary? Brain-computer interface robots enabling paralyzed patients to control exoskeletons via thought alone. These weren't predicted even in Minority Report's 2054 setting.
The AI Surgeon's Toolkit: 5 Breakthrough Technologies
Smart Suturing Bots: Autonomous stitching with real-time tissue analysis (reduces scarring by 70%)
Nanodrone Swarms: Thousands of microbots delivering drugs precisely to tumors
Holographic Guidance: AR overlays showing surgeons hidden blood vessels and nerves
Self-Learning Surgical AI: Systems that improve technique by analyzing millions of past procedures
Bioprinting Robots: 3D printing living tissue directly onto wounds during operations
Why Hospitals Can't Resist the Robotic Revolution
The data speaks volumes: robotic-assisted surgeries account for 1.5 million procedures annually (Surgical Robotics Market Report, 2024). Key advantages driving adoption include 83% shorter hospital stays (Mayo Clinic data) and sub-millimeter precision eliminating hand tremors. Surprisingly, malpractice claims dropped 42% in robot-assisted cases versus traditional methods (AMA 2023 report). Patients report 68% higher satisfaction scores when treated with robotic systems, citing smaller incisions and faster recovery.
Ethical Dilemmas: The Dark Side Sci-Fi Warned Us About
As Medical Robots from Science Fiction to Science Fact become mainstream, ethical quandaries emerge. Who's liable when an AI surgeon makes an error? Can hacked surgical bots become weapons? The 2024 Brussels Protocol established global standards requiring: (1) human override capability, (2) encrypted neural networks, and (3) mandatory "explainability" for all AI medical decisions. These guardrails aim to prevent real-world equivalents of HAL 9000's malfunctions while enabling innovation.
FAQs: Answering Your Top Medical Robotics Questions
1. Are robotic surgeries safer than human-performed ones?
Current data suggests yes—when performed by trained surgeons using robotic assistance. The da Vinci system demonstrates 30% fewer complications in prostate surgery (New England Journal of Medicine, 2023). However, the technology doesn't replace surgeon skill; it enhances precision where human physiology has limitations like hand tremors or restricted visibility.
2. Will medical robots replace human doctors entirely?
Unlikely in our lifetime. While robots excel at repetitive, precision tasks, they lack human judgment for complex cases. The future lies in collaboration—AI handling diagnostics and routine procedures, freeing doctors for patient care and complex decision-making. IBM's 2024 survey shows 78% of patients still prefer human doctors for final treatment decisions.
3. How much do these robotic systems cost hospitals?
Prices range from $500,000 for basic assistance bots to $2.5 million for full surgical systems. However, hospitals recoup costs through: (1) higher procedure volumes (robots enable 3x more daily surgeries), (2) reduced complication costs, and (3) premium pricing. Most institutions break even within 3 years (Healthcare Economics Review, 2024).
The Next Frontier: 2030 Predictions That Sound Like Sci-Fi Today
Researchers are developing: (1) DNA-repair nanobots to reverse aging damage, (2) neural lace implants for instant surgical skill downloads, and (3) autonomous emergency trauma bots for battlefield use. MIT's 2024 prototype already demonstrated a self-contained robotic surgeon that could perform appendectomies aboard the International Space Station—no human intervention needed. The line between Medical Robots from Science Fiction to Science Fact continues blurring at breathtaking speed.
Conclusion: The Future Is Here—Just Not Evenly Distributed
What was once confined to Asimov's pages and Spielberg's screens now saves lives daily in operating rooms worldwide. While challenges around cost and access persist (only 12% of African hospitals have robotic systems versus 94% in North America), the Medical Robots from Science Fiction to Science Fact revolution proves that with enough innovation and ethical oversight, humanity's most ambitious healing fantasies can become its greatest medical achievements.