Imagine a surgeon performing heart surgery with superhuman precision or a robot disinfecting entire hospital wards in minutes. The integration of robotics in healthcare isn't science fiction—it's today's reality. Medical Robots Uses tackle critical challenges like surgical accuracy, infection control, and accessible diagnostics, fundamentally transforming patient outcomes globally. With global AI-driven robotic healthcare poised to exceed $32 billion by 2030, these innovations are redefining standards of care while slashing human error rates by up to 80%.
Why Medical Robots Uses Are Revolutionizing Healthcare
The healthcare sector has witnessed unprecedented advancements through robotic technology. Unlike traditional methods, Medical Robots Uses provide consistent precision, reduce recovery times, and enable procedures previously deemed impossible. From neurosurgery to rehabilitation, these intelligent systems combine AI algorithms with mechanical precision to deliver outcomes that consistently outperform human capabilities in specific applications.
The Medical Robotics Revolution: How da Vinci Became the World's Most Famous Surgical Assistant
1. Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Precision Beyond Human Capability
The da Vinci Surgical System represents the gold standard in robotic surgery, enabling procedures with sub-millimeter accuracy. These systems translate a surgeon's hand movements into smaller, precise motions, allowing for minimally invasive procedures with 3D visualization. Studies show robotic surgery reduces patient blood loss by 52% and lowers complication rates by 32% compared to traditional methods.
2. Telepresence Robots: Bridging the Specialist Gap
Remote presence robots equipped with high-definition cameras and microphones enable specialists to consult across vast distances. Particularly valuable in rural areas, these systems provide real-time diagnostics and treatment recommendations. During the COVID-19 pandemic, telepresence robot usage surged by 400%, demonstrating their critical role in maintaining healthcare continuity.
3. Disinfection Robots: The UV-C Guardians
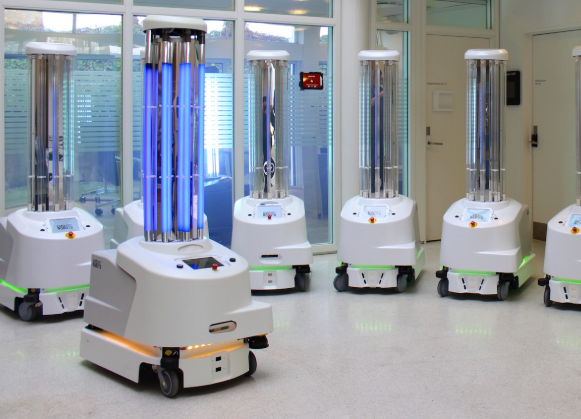

Autonomous UV disinfection robots like Xenex's LightStrike eliminate pathogens in hospital rooms with 99.99% efficacy. These systems complete room sterilization in 10-15 minutes—a process that would take human staff hours. Hospitals implementing these robots report 50-70% reductions in healthcare-associated infections, directly saving lives and reducing costs.
4. Exoskeletons: Restoring Mobility
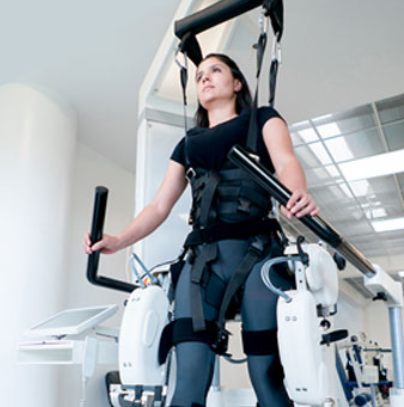

Rehabilitation robots such as EksoGT help stroke and spinal cord injury patients regain movement through powered exoskeletons. Clinical trials demonstrate that robotic-assisted therapy improves walking speed by 150% compared to conventional methods. These devices adapt to each patient's progress, providing personalized rehabilitation protocols.
5. Pharmaceutical Robots: Error-Free Medication Dispensing
Automated pharmacy systems like ScriptPro accurately dispense medications at rates of up to 150 prescriptions per hour with 100% accuracy. These robots reduce medication errors—the third leading cause of death in healthcare—by eliminating human factors in dosage calculations and labeling.
6. Robotic Prosthetics: Bionic Advancements
Next-generation prosthetic limbs with neural interfaces and AI processors interpret muscle signals to provide natural movement. The LUKE Arm, for instance, offers 10 distinct grip patterns and haptic feedback, enabling users to perform delicate tasks like picking grapes or typing on keyboards.
7. AI Diagnostic Robots: Early Detection Specialists
IBM Watson Health's AI systems analyze medical images with greater accuracy than human radiologists for certain conditions. In mammography, these systems detect microcalcifications—early signs of breast cancer—with 97% accuracy versus the human average of 92%.
8. Robotic Nurse Assistants: 24/7 Patient Care
Robots like Moxi handle logistical tasks—delivering supplies, transporting lab samples—freeing nurses to focus on direct patient care. Hospitals using nurse assistant robots report 30% reductions in nurse fatigue and 20% improvements in patient satisfaction scores.
9. Microbots: The Future of Targeted Therapy
Researchers at ETH Zurich developed microrobots that navigate blood vessels to deliver drugs precisely to tumors. These 10-micron devices reduce chemotherapy side effects by concentrating medication at the disease site while sparing healthy tissue.
10. Robotic Lab Technicians: High-Throughput Testing
Automated lab systems process thousands of tests daily with robotic precision. During peak pandemic demand, these systems increased COVID-19 testing capacity by 500% while maintaining 99.8% accuracy rates—a feat impossible with manual processing.
FAQs About Medical Robots Uses
How safe are surgical robots compared to human surgeons?
Robotic surgery systems have demonstrated superior safety in complex procedures. The da Vinci system, for example, shows 21% fewer complications in prostatectomies compared to open surgery. However, they require specialized surgeon training and aren't suitable for all procedures.
Will medical robots replace healthcare workers?
Robots augment rather than replace human staff. The World Health Organization projects a global shortage of 18 million healthcare workers by 2030—robots will help bridge this gap by handling repetitive tasks while humans focus on complex decision-making and patient interaction.
What's the cost-benefit analysis for hospitals implementing robotic systems?
While initial investments are substantial ($1-2 million for surgical systems), hospitals report ROI within 2-3 years through shorter hospital stays (average 1.5 days reduction) and lower readmission rates (15-20% decrease). Disinfection robots show even faster ROI—about 9 months—through infection reduction savings.
The Future of Medical Robots Uses
Emerging technologies promise even more revolutionary applications. Nanorobots for targeted drug delivery, AI-powered robotic psychiatrists for mental health care, and autonomous trauma response systems are already in advanced testing phases. As these systems become more sophisticated and affordable, they'll transition from hospital exclusives to standard community healthcare tools.