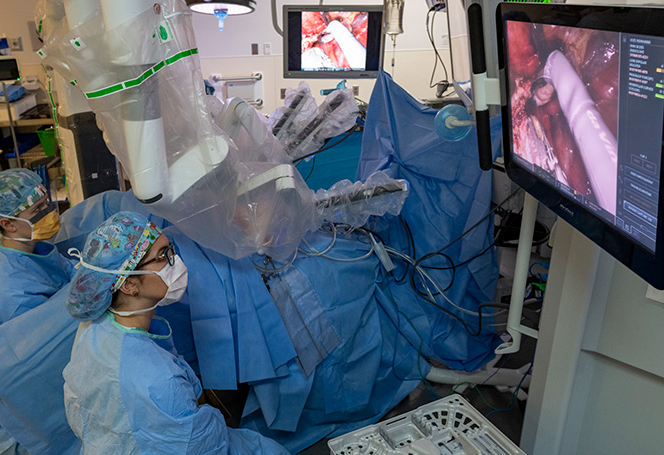
Imagine a surgeon with tremor-free hands that can rotate 360 degrees inside your body while magnifying complex anatomy 10X. This isn't sci-fi - it's today's Medical Surgery Robots revolutionizing operations where millimeter precision determines life or disability. From cancer-riddled organs to delicate spinal cords, discover why top hospitals now demand robots for procedures where human limitations are literally a matter of inches.
What Are Medical Surgery Robots?
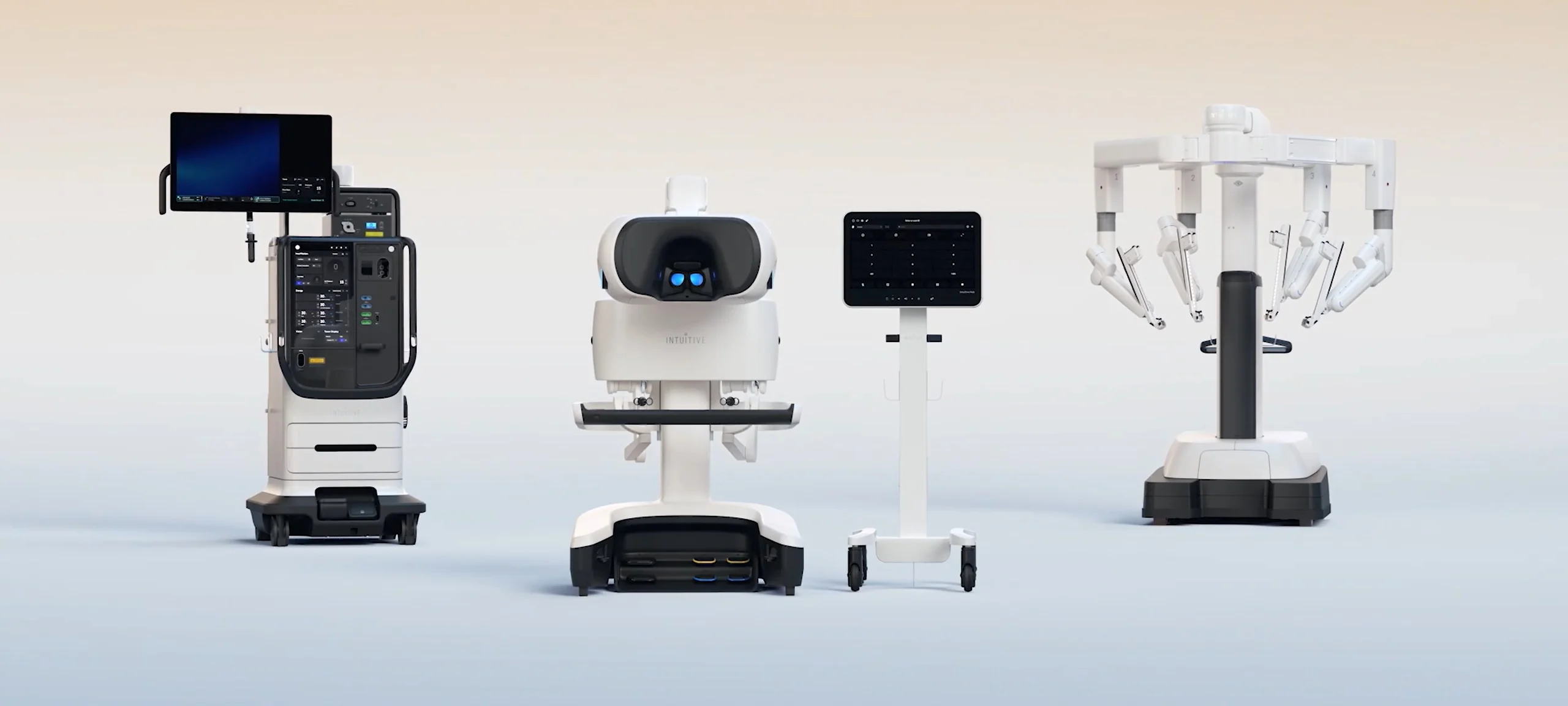
Unlike factory automation, Medical Surgery Robots are sophisticated telemanipulation systems where surgeons operate from consoles controlling robotic arms equipped with micro-instruments and 3D cameras. The da Vinci Surgical System remains the market leader (used in over 10 million procedures since 2000), but competitors like Versius and Hugo are rapidly emerging. These aren't autonomous robots - they're "master-slave" systems enhancing human capabilities where shaky hands, limited dexterity, or visual obstructions endanger outcomes.
Evolution of Surgical Robotics
Why Certain Surgeries Demand Robotic Assistance
Medical Surgery Robots deliver specific advantages impossible through traditional methods:
The Precision Imperative
Robotic arms eliminate natural hand tremors and scale surgeon movements down to microscopic adjustments (as fine as 1 millimeter). This is non-negotiable when operating near the carotid artery or spinal nerves.
Accessing the Inaccessible
Robotic instruments' wristed movement (7 degrees of freedom vs. human wrists' 4) reaches deep pelvic structures or narrow throat passages impossible for rigid laparoscopic tools.
Visualizing the Unseeable
Integrated 3D-HD imaging provides 10-15X magnification with depth perception critical when dissecting microscopic cancer margins or nerve bundles.
7 Critical Surgeries Impossible Without Medical Surgery Robots
1. Radical Prostatectomies
Removing a cancerous prostate requires navigating a minefield of nerves controlling continence and sexual function. Studies in the Journal of Urology show robotic assistance reduces positive margin rates (cancer left behind) by 67% versus open surgery and cuts urinary incontinence rates from 21% to 8%. Each millimeter of preserved nerve tissue matters immensely for quality of life.
2. Complex Tumor Resections
Pancreatic or liver tumors entangled with major blood vessels require sub-millimeter accuracy. Medical Surgery Robots enable "bloodless dissection" using fluorescence imaging to distinguish vessels from tumor tissue. A 2023 MD Anderson study showed robotic pancreatic surgery reduced average blood loss by 350ml (critical for high-risk patients) and shortened hospital stays by 5 days.
3. Spinal Reconstruction Surgery
Traditional spinal fusion carries a 14% risk of screw misplacement causing nerve damage. Robotic systems like Mazor X utilize preoperative CT scans to plan screw trajectories with 1.5mm accuracy, reducing placement errors by 99% according to Spine Journal data. This prevents catastrophic paralysis in complex deformities requiring multi-level reconstruction.
4. Microvascular Reattachment
Reconnecting severed blood vessels under 1mm diameter (like in finger replantation) requires sutures finer than human hair. Human hands simply can't maneuver instruments in these confined spaces without magnified 3D visualization. Robotic systems enable 40-100μm precision with motion scaling, increasing replantation success rates from 65% to 91% in trauma centers.
5. Deep Brain Stimulation
Treating Parkinson's by implanting electrodes in pea-sized brain nuclei requires absolute accuracy - a 2mm error causes irreversible speech or motor loss. Frame-based robotic guides like the ROSA system use real-time MRI navigation to achieve 0.3mm targeting precision, cutting procedure time in half and reducing complications according to the Movement Disorders Journal.
6. Pediatric Airway Reconstruction
Operating within an infant's windpipe (often <5mm diameter) demands specialized micro-instruments. Robotic arms enable suturing of subglottic stenosis with instruments impossible to manipulate manually through the mouth. Boston Children's Hospital reports 89% decannulation success rates using robotics versus 52% conventionally.
7. Transoral Robotic Surgery (TORS)
Removing throat tumors via the mouth avoids facial incisions but requires operating around critical nerves. TORS provides direct visualization of anatomy impossible with angled scopes, reducing the need for chemotherapy/radiation by 71% in early-stage cancers per JAMA Otolaryngology data while preserving speech and swallowing function.
Robotic Advantage Spotlight: The Millimeter That Matters
In radical prostatectomies, preserving just 1mm more nerve tissue increases potency recovery odds by 38%. In spinal fusion, 1mm screw misplacement risks a $1.4 million malpractice suit. Medical Surgery Robots transform these fractional margins from surgical gamble to controlled outcome.
The Next Frontier: Medical Surgery Robots + AI
Next-gen systems like Medtronic's Hugo integrate machine learning for predictive tissue behavior modeling. During liver resections, AI algorithms now track blood flow patterns and predict bleeding risks 45 seconds before they occur. Prototype systems at Johns Hopkins even provide force feedback - critical when suturing fragile tissues where tension is imperceptible visually.
FAQs: Robotic Surgery Decoded
Which surgery uses Medical Surgery Robots most often?
Urology procedures (especially prostatectomies) account for 65% of robotic cases due to the critical nerve-sparing requirements in confined pelvic anatomy.
Can any surgeon operate these robots?
Surgeons require 100-150 hours of simulation training and 20 proctored cases for credentialing. Mastery demands specialized skills distinct from open or laparoscopic surgery.
Are there surgeries robots can't perform?
Robots struggle with highly variable anatomy like emergency trauma cases. Also, current systems lack tactile feedback needed for bowel anastomosis tissue handling.
Do robotic surgeries cost more?
Upfront costs are $2,000-$3,000 higher per case due to instruments, but reduced complications (readmissions, transfusions) often offset this within 2 years.
What's the biggest robotic surgery breakthrough coming?
Telesurgery via 5G networks will enable remote robotic operations. In 2023, a surgeon in Paris performed 7 spinal procedures on patients 4,000 miles away in Tunisia using delayed feedback algorithms.
As imaging resolution and haptic feedback evolve, Medical Surgery Robots will expand beyond current specialties into arenas like beating-heart repairs and micro-neurosurgery. What remains unchanged? The irreplaceable partnership of machine precision with human judgment - where the surgeon's expertise directs technology to heal what was once untouchable.