China's Pioneering Underwater Robots Examples
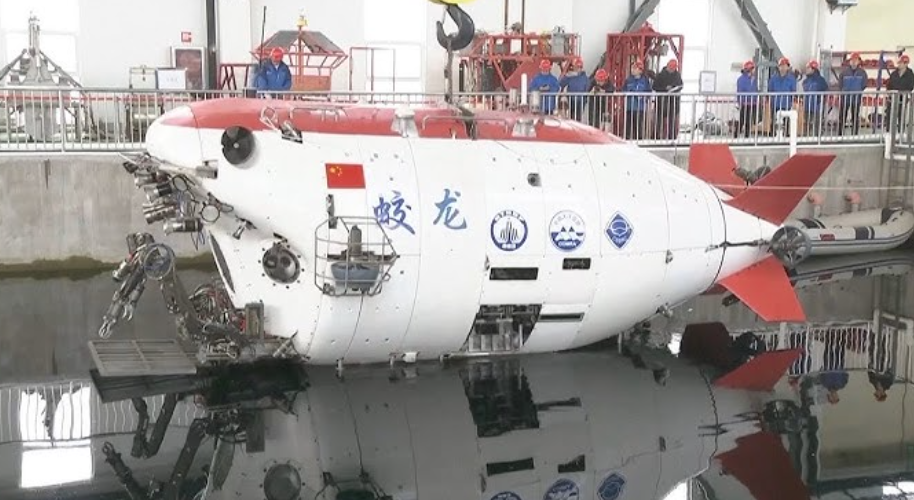

China's Jiaolong manned submersible made history in 2012 by reaching 7,062 meters in the Mariana Trench, setting a national record for deepest dive. This remarkable Underwater Robot Example can carry three people to extreme depths for scientific research, equipped with robotic arms, high-definition cameras, and advanced sampling systems. Named after a mythical dragon, Jiaolong has completed over 150 successful dives, exploring hydrothermal vents and collecting precious deep-sea specimens.
The Haima remotely operated vehicle (ROV) represents China's breakthrough in underwater resource exploration. This Underwater Robot Example specializes in detecting and sampling gas hydrates - the "flammable ice" that could revolutionize energy supplies. In 2017, Haima successfully collected samples from the South China Sea at 1,400 meters depth, demonstrating China's growing capabilities in underwater resource exploitation while minimizing environmental impact.
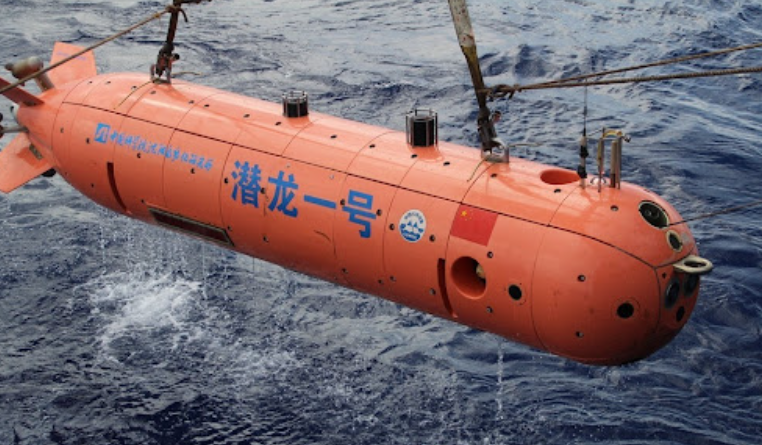

China's Qianlong series of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) showcase the nation's advancements in untethered deep-sea exploration. The Qianlong-3, capable of operating at 6,000 meters depth, uses AI-powered navigation to conduct seabed surveys for up to 30 hours. These Underwater Robots Examples are equipped with multi-beam sonar, magnetometers, and cameras, making them invaluable for mineral exploration and underwater pipeline inspection.
Breaking new ground in 2020, China's Haidou-1 became the world's first autonomous submersible to reach the bottom of the Mariana Trench. This remarkable Underwater Robot Example achieved a depth of 10,908 meters, demonstrating China's ability to compete with Western deep-sea technology. Haidou's success marked a significant milestone in China's "Deep Sea Tiger" program, showcasing advanced pressure-resistant materials and AI navigation systems.
Developed by Shenyang Institute of Automation, the SeaWhale 2000 represents China's growing expertise in industrial underwater robotics. This versatile Underwater Robot Example specializes in dam inspections, bridge maintenance, and underwater structure monitoring. Equipped with 4K cameras, laser scanners, and ultrasonic thickness gauges, it can operate in strong currents while maintaining millimeter-level positioning accuracy - crucial for infrastructure safety.
The CR series marked China's first successful foray into deep-sea autonomous robots. The CR-02, developed in the 1990s, could reach 6,000 meters depth and was instrumental in surveying the Pacific Ocean floor for polymetallic nodules. These early Underwater Robots Examples laid the foundation for China's current generation of sophisticated AUVs, demonstrating the nation's long-term commitment to ocean exploration.
Representing China's push into commercial underwater robotics, the SeaFly series offers affordable, portable ROVs for research and industry. These compact Underwater Robots Examples feature modular designs allowing customization with various sensors and tools. Popular among marine researchers and underwater photographers, SeaFly drones demonstrate how China is democratizing access to underwater exploration technology.
Learn More About Underwater Robots Capabilities
Technological Breakthroughs in Chinese Underwater Robots Examples
Advanced Materials and Pressure Resistance
Chinese engineers have developed innovative titanium alloys and ceramic composites that can withstand extreme pressures at depths exceeding 10,000 meters. These materials are crucial for housing sensitive electronics and maintaining structural integrity in the most challenging underwater environments.
AI-Powered Navigation Systems
China's latest Underwater Robots Examples incorporate machine learning algorithms that enable autonomous decision-making in unpredictable underwater conditions. These systems can adapt to changing currents, avoid obstacles, and optimize survey paths without human intervention.
Underwater Communication Innovations
Breakthroughs in acoustic communication allow China's underwater robots to maintain data links at greater depths and distances. Some systems now use hybrid acoustic-optical communication for high-bandwidth data transmission in clear waters.
Explore Different Underwater Robot Types
Applications of China's Underwater Robots Examples
Scientific Research and Exploration
From studying deep-sea ecosystems to investigating hydrothermal vents, Chinese underwater robots are expanding our understanding of marine science. The Jiaolong submersible has been instrumental in discovering new species and studying underwater geology.
Resource Exploration and Mining
China's growing need for mineral resources has driven development of underwater robots capable of surveying and sampling polymetallic nodules, gas hydrates, and rare earth elements on the ocean floor.
Defense and Security Applications
While details are often classified, China's military has invested heavily in underwater robotics for mine detection, harbor security, and underwater surveillance applications.
Frequently Asked Questions About Underwater Robots Examples in China
Chinese underwater robots often emphasize cost-effectiveness and modular designs while incorporating unique pressure-resistant materials developed specifically for deep-sea conditions. Many systems are optimized for resource exploration applications in the South China Sea region.
While China started later than Western nations in underwater robotics, recent achievements like the Haidou-1's Mariana Trench dive demonstrate they've closed much of the technological gap. China now leads in certain areas like deep-sea resource exploration robots and cost-effective commercial ROVs.
Some commercial models like the SeaFly series are available internationally, but China's most advanced underwater robots are primarily used by domestic research institutions and government agencies. Joint international research projects sometimes provide limited access to these technologies.
The Future of Chinese Underwater Robotics
China's impressive array of Underwater Robots Examples demonstrates the nation's strategic commitment to dominating deep-sea exploration and resource exploitation. As technology advances, we can expect even more sophisticated autonomous systems, deeper diving capabilities, and broader applications across scientific, commercial, and defense sectors. These underwater robots not only serve practical purposes but also symbolize China's growing technological prowess on the global stage.