What Exactly is a Space Exploration Robot?
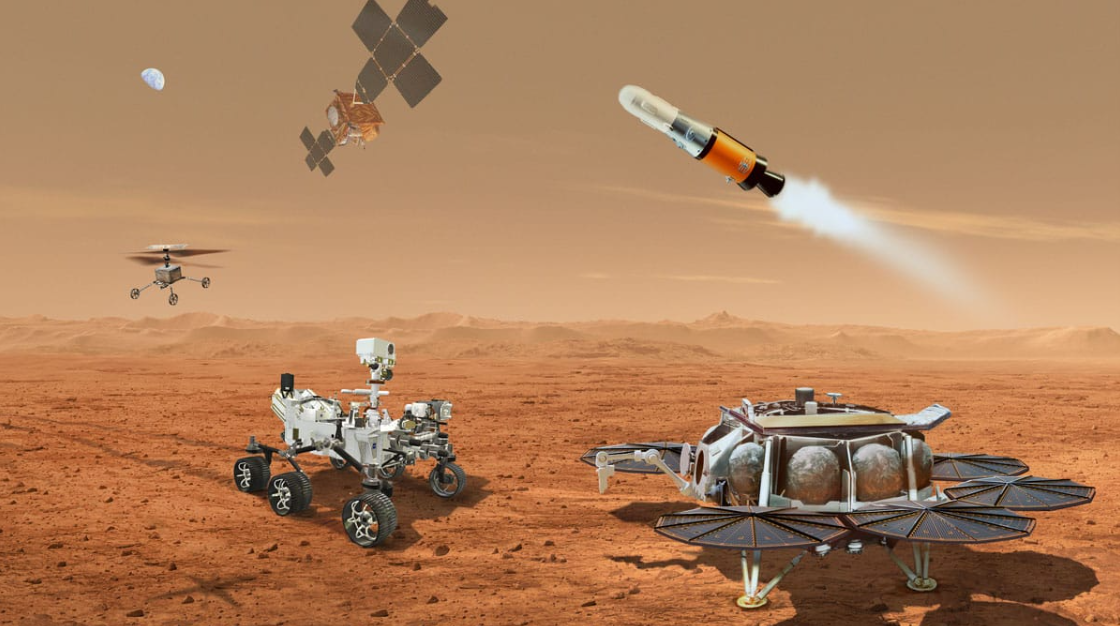
A Space Exploration Robot is an uncrewed machine explicitly designed to operate autonomously or semi-autonomously in the extreme conditions of space or on celestial bodies. Unlike industrial robots tethered to Earth, these explorers possess unique capabilities:
Radiation-Hardened Electronics: Surviving intense cosmic rays that fry ordinary circuits.
Extreme Environment Adaptation: Functioning in hard vacuums, cryogenic cold, or searing heat.
Advanced AI for Autonomy: Making real-time decisions despite communication delays (e.g., Mars rover decisions take 4-24 minutes roundtrip).
Scientific Instrumentation: Carrying miniaturized labs like spectrometers, drills, and microscopes.
Their core purpose is scientific discovery and reconnaissance, venturing where humans cannot. You can learn more about their revolutionary purpose in our deep dive into exploration robotics: Uncharted Realms: What is an Exploration Robot & Why They're Revolutionizing Discovery.
Core Architectures of Modern Space Exploration Robots
Rovers: Wheeled or tracked platforms for surface exploration (e.g., NASA's Perseverance, ESA's planned Rosalind Franklin).
Landers: Stationary platforms analyzing landing sites (e.g., NASA's InSight Mars Lander, JAXA's Hayabusa2 MASCOT).
Orbiters: Satellites mapping and analyzing planets/moons from above (e.g., ESA's JUICE mission to Jupiter's moons).
Probes: Deep-space craft gathering data during flybys (e.g., NASA's Voyager, New Horizons).
The Evolution Saga: From Sputnik to AI-Driven Pioneers
The journey of the Space Exploration Robot is a testament to relentless engineering ingenuity:
1950s-60s (The Pioneers): Simple probes like Luna 2 (first human object on Moon) and Mariner 2 (first Venus flyby). Minimal autonomy, basic telemetry.
1970s-90s (Surface Scouts Emerge): Lunokhod 1 (1970, first remote-controlled rover on Moon). Viking Landers (1976, first life-searching experiments on Mars). Increasingly complex instruments.
1997-Present (Rover Renaissance): Sojourner (1997, first Mars rover), Spirit/Opportunity (2004, revolutionised longevity expectations), Curiosity (2012, car-sized lab).
2020s (AI Autonomy Era): Perseverance (2020) with self-driving AI and helicopter scout Ingenuity. Robotic arms on ISS like Canadarm2 assembling stations and capturing cargo ships.
AI & Machine Learning: The Game Changer
Modern Space Exploration Robots aren't just remote-controlled puppets. They leverage cutting-edge AI:
Autonomous Navigation (AutoNav): Generating safe paths around obstacles in real-time using stereo cameras (Perseverance drives 100+ meters autonomously).
Target Selection: Using onboard AI to identify scientifically valuable rocks/deposits without waiting for Earth commands.
Self-Diagnosis & Healing: Identifying hardware/software faults and implementing workarounds to continue operations.
This shift from teleoperation to autonomy is critical for exploring moons like Europa, where light-speed delays make real-time control impossible.
Why Space Exploration Robots Revolutionize Discovery
Space Exploration Robots aren't just replacements for humans; they enable entirely new scientific paradigms. They unlock discoveries impossible for astronauts:
Accessing the Impossible: Exploring Venus's surface (462°C, 92x Earth's pressure), Jupiter's radiation belts, Saturn's moon Enceladus's subsurface ocean jets.
Endurance & Cost: Operating continuously for years/decades at a fraction of crewed mission costs (Curiosity rover cost ~$2.5B vs. estimated $500B+ for crewed Mars mission).
Precision & Contamination Control: Conducting delicate searches for biosignatures without contaminating environments with Earth microbes.
Foundation for Humanity: Scouting resources (water ice!), mapping terrain, and testing technologies essential for future human outposts.
Discover the profound impact of these robotic trailblazers in our dedicated article: Uncharted Realms: What is an Exploration Robot & Why They're Revolutionizing Discovery.
Iconic Robotic Trailblazers: Reshaping Our Cosmic Knowledge
Specific Space Exploration Robots have fundamentally altered our cosmic perspective. While familiar names exist, true revolutionaries include:
Voyager 1 & 2 (1977): Now in interstellar space, carrying the Golden Record – humanity's farthest-reaching emissaries.
ESA's Rosetta/Philae (2014): First to orbit and land on a comet (67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko), revealing complex organic molecules.
Hayabusa2 (JAXA, 2018-2020): Performed precision touchdown on asteroid Ryugu, collected subsurface samples revealing water and organics.
NASA's InSight Lander: Uncovering Mars' seismic heart (detecting "marsquakes") to reveal its internal structure.
Dragonfly (NASA, Launch 2027): Nuclear-powered drone designed to fly through Titan's atmosphere, seeking prebiotic chemistry.
Explore the mind-bending achievements of these and other robotic explorers: Unbelievable Exploration Robots Examples Rewriting Earth & Cosmic Discovery.
Beyond Mars & Moon: The Next Frontier for Space Exploration Robots
The future is incredibly diverse for robotic explorers:
Ocean Worlds: Europa Clipper orbiter (NASA), JUICE mission to Ganymede (ESA) – probing subsurface oceans for potential life. Robots for drilling through ice miles thick.
Asteroid Mining Prospectors: Commercial robots surveying resources on NEOs (Near-Earth Objects).
Lunar Infrastructure Builders: NASA's CADRE project aims for teams of small rovers building structures autonomously.
Interstellar Precursors: Concepts like Breakthrough Starshot envision tiny, laser-propelled probes flying to Alpha Centauri.
Self-Replicating Von Neumann Probes: A theoretical future where robots mine asteroids to build copies of themselves, exponentially expanding reach.
Overcoming Cosmic Hurdles: Challenges Facing Space Exploration Robots
Operating in space pushes engineering to its breaking point:
Harsh Environment: Radiation degradation, extreme temperatures (-270°C to +450°C), abrasive dust (Mars), lack of atmosphere/gravity.
Communication Lag: Deep-space robots often need near-full autonomy due to minutes/hours of light delay.
Power Limitations: Relying on solar panels (diminishing with dust/distance) or limited RTGs (Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators).
Single-Point Failures: Redundancy is weight-prohibitive; a single key component failure can end a billion-dollar mission.
Software Complexity: Millions of lines of code require flawless operation under unpredictable conditions.
Humanity's Silent Partners: Robots Paving the Way for Us
The ultimate legacy of Space Exploration Robots is enabling the future of human spaceflight:
Resource Prospecting: Locating accessible water ice (crucial for fuel, oxygen, water) on the Moon and Mars.
Hazard Mapping: Identifying safe landing zones, radiation hotspots, and unstable terrain.
Technology Demonstrators: Testing ISRU (In-Situ Resource Utilization), radiation shielding, and life support systems.
Infrastructure Precursors: Robotic assembly of habitats, power grids, and landing pads before human arrival.
Robots are the indispensable pathfinders for humanity's expansion into the solar system.
Space Exploration Robot FAQs: Your Burning Questions Answered
Q1: What's the most successful Space Exploration Robot ever?
A: Arguments abound, but Voyager 1/2 (over 45 years operation, now interstellar) & the Mars rover Opportunity (operated 15 years vs. 90-day plan!) are legendary. Scientifically, the Hubble Space Telescope (though an observatory, technically a complex robot) tops the list.
Q2: Can these robots truly "think" for themselves?
A: They don't possess consciousness or generalized AI. Modern robots use highly specialized AI for specific tasks (pathfinding, target selection, fault detection) within predefined parameters. Decision-making is bounded autonomy.
Q3: What happens to these robots when their missions end?
A: Functional robots become historical monuments on their worlds (e.g., Spirit, Opportunity, Zhurong rovers). Orbiters sometimes crash into planets/moons or are sent into "graveyard" orbits. Functional ones like Voyager continue streaming data until they die.
Q4: How likely are robots to find extraterrestrial life?
A: Robots are our best chance in the near term. Missions targeting ocean worlds (Europa, Enceladus, Titan) and Mars' ancient past are specifically designed to detect evidence of past or present microbial life. They carry instruments humans couldn't replicate onsite.
Conclusion: The Robots Who Dreamed the Stars
The epoch of the Space Exploration Robot has fundamentally transformed us from passive stargazers into active cosmic explorers. These resilient machines are not mere tools; they are extensions of human curiosity and intellect, embodying our relentless drive to understand the universe. They brave environments where flesh and bone would instantly perish, turning the abstract realms of distant worlds into concrete landscapes ripe for study. As AI evolves, solar sails deploy, and drills probe icy moons, these robotic pioneers promise discoveries more staggering than we can currently imagine. They are rewriting history, not with ink, but with binary code transmitted across the void, proving that to explore the infinite cosmos, we must first master the art of sending our most ingenious machines beyond the cradle.


