Imagine a driving test where the examiner never gets tired, never has a bad day, and possesses superhuman perception to analyze every micro-movement of your vehicle. This is no longer science fiction. The Driving Test Robot is here, and it is fundamentally reshaping how we certify drivers. Moving beyond the subjective human glance, these AI-powered systems deploy a complex array of sensors and algorithms to deliver a perfectly objective, hyper-accurate, and utterly fair assessment of driving competence. This article delves deep into the technology, the benefits, the global implementation, and the profound ethical implications of handing over the driver's test to artificial intelligence.
What is a Driving Test Robot? Deconstructing the Technology
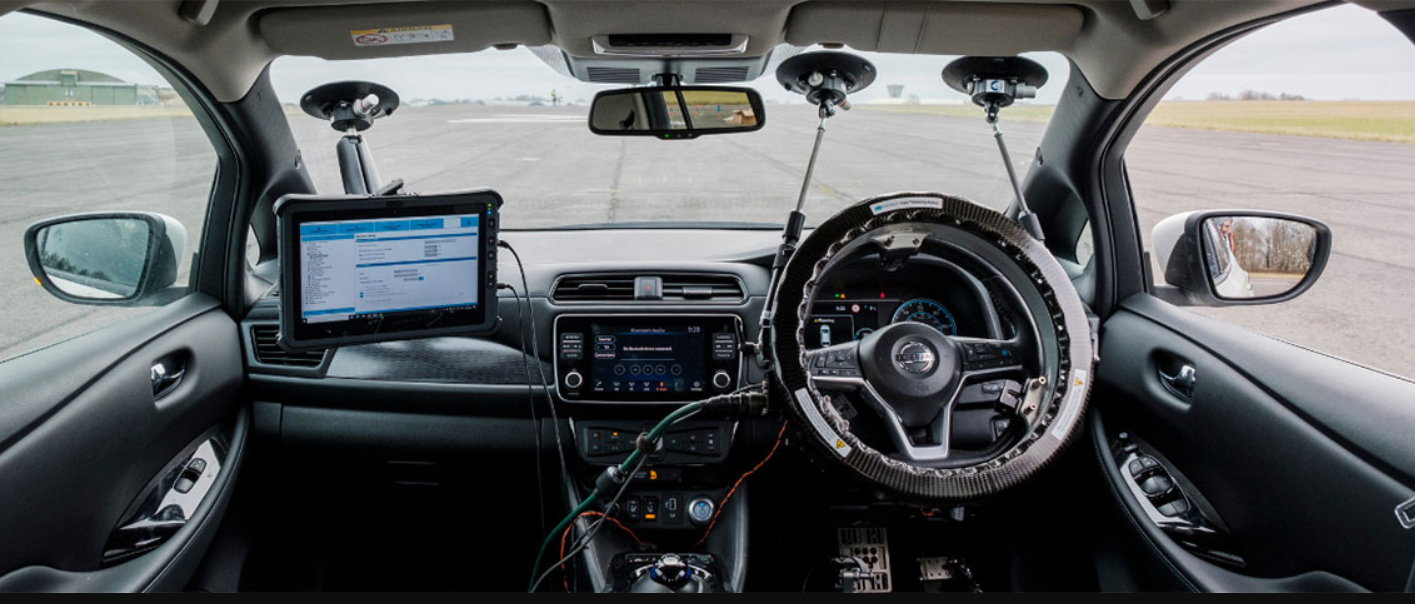
At its core, a Driving Test Robot is an integrated artificial intelligence system designed to autonomously administer and evaluate a practical driving examination. It is not a physical robot sitting in the passenger seat but a sophisticated suite of technologies installed within a test vehicle. The system typically comprises high-precision GPS, inertial measurement units (IMUs), LIDAR, cameras, and a powerful onboard computer. The AI synthesizes this real-time sensor data to build a dynamic 4D model of the vehicle's environment, tracking its position, speed, acceleration, and proximity to obstacles with centimeter-level accuracy. This allows it to objectively detect violations, errors, and the overall safety of the driver's performance against a pre-programmed set of rigorous criteria.
Beyond Human Limits: The Unmatched Advantages of Robotic Examiners
The adoption of Driving Test Robot technology is driven by its significant advantages over human-based testing. First and foremost is the elimination of subjectivity and bias. A human examiner might be influenced by a candidate's appearance, gender, or nervousness; the AI judge is completely impartial. Secondly, its perception is limitless. It can simultaneously monitor road positioning, mirror usage, steering smoothness, pedal control, and blind spot checks without ever missing a detail. This leads to enhanced consistency; every candidate is assessed by the exact same standard, ensuring a fair and uniform licensing process. Furthermore, it increases efficiency, allowing testing centers to conduct more exams daily with reduced human resource costs.
How the Machine Judges: A Step-by-Step Tutorial on the Assessment Algorithm
Understanding how the AI evaluates a drive demystifies the process. The algorithm follows a complex but logical decision-tree model.
Pre-drive Calibration: The system initializes, confirming all sensors are operational and establishing a precise geo-fence for the test route.
Real-time Data Acquisition: Throughout the drive, sensors continuously feed data into the central processing unit. Cameras track lane discipline and traffic light compliance, LIDAR maps the proximity to curbs and other vehicles, and IMUs record G-forces during turns and braking.
Pattern Recognition and Analysis: The AI compares the live data against a database of ideal and dangerous driving patterns. For example, a sudden swerve is flagged as a potential loss of control, while smooth acceleration is scored positively.
Error Logging and Scoring: Minor faults (e.g., slight overspeed) and major faults (e.g., failing to stop at a stop sign) are logged instantly. The algorithm weights these errors to calculate a final score.
Post-test Report Generation: Immediately after the test, the system generates a comprehensive digital report, itemizing every fault with precise timestamps and sensor data, providing candidates with invaluable feedback for improvement.
A Global Phenomenon: Where Driving Test Robots Are Already on the Road
While it may seem futuristic, Driving Test Robot technology is already deployed in several countries. China has been a pioneer, implementing these systems in multiple major cities like Beijing and Shanghai to combat high failure rates and allegations of corruption in the manual testing process. The results have been stark, with reported pass rates initially plummeting as the AI exposed common errors previously missed by human examiners. Other nations, including the UK and Japan, are running advanced pilot programs. This global trend indicates a rapid shift towards automated assessment as the gold standard for driver licensing, a key milestone in the broader journey toward autonomous vehicle technology.
The Ethical Roadblock: Addressing Concerns Over Fairness and Accessibility
The rise of the Driving Test Robot is not without controversy. Critics raise valid concerns about the "dehumanization" of the test. Can an algorithm understand context? For instance, a human examiner might forgive a slightly late signal due to complex traffic, while a strict algorithm may penalize it. There are also fears about system errors, such as GPS glitches leading to false failures. Furthermore, the high cost of implementing this technology could widen the gap between wealthy and developing regions, creating a disparity in driving standards. These ethical dilemmas require careful regulation and transparent oversight to ensure the technology serves justice and safety without creating new forms of inequity.
FAQs: Your Questions About Driving Test Robots Answered
Can a Driving Test Robot be tricked or cheated?
It is significantly more difficult to cheat an AI examiner than a human. The system monitors and cross-references multiple data points simultaneously. For example, while a candidate might remember to overtly turn their head to check a blind spot (fooling a camera), the algorithm might still flag a fault if the steering input began before the head movement was registered, indicating the maneuver was not preceded by a proper check. Its holistic analysis makes deception extremely challenging.
What happens if the Driving Test Robot malfunctions during my test?
Reputable systems are built with robust redundancy and fail-safes. If a critical sensor fails, the test is typically automatically halted and declared void. The data from the drive is saved and can be reviewed by a human supervisor to determine if the test can be resumed or must be retaken at a later date, usually at no cost to the candidate. The principle is to ensure no applicant is unfairly disadvantaged by a technical fault.
Will Driving Test Robots eventually replace human examiners entirely?
While the trend is toward greater automation, a fully unmanned future is unlikely in the short term. The most probable scenario is a hybrid model. The Driving Test Robot handles the objective assessment of vehicle control and traffic law adherence, while a human examiner remains in the vehicle to oversee the test, manage safety, and evaluate softer skills like customer interaction and judgment in unpredictable situations that still challenge AI. This combines the best of both worlds.