In a world where science fiction is becoming reality, the concept of a Humanoid Robot captures our imagination. From movies to real-world applications, these robots are designed to mimic human appearance, movements, and even decision-making. But how does a Robot That is Like a Human actually work? Is it possible to make a robot that looks like a human and functions seamlessly in our society? This article dives deep into the technology, mechanics, and ethical debates surrounding humanoid robots, with a focus on real-world examples like Atlas and Sophia.
What is a Humanoid Robot?
A Humanoid Robot is a machine designed to resemble and emulate human physical characteristics and behaviors. Unlike industrial robots confined to assembly lines, humanoid robots are built to interact with humans in dynamic environments, such as homes, hospitals, or public spaces. They combine artificial intelligence (AI), advanced mechanics, and sensory systems to perform tasks ranging from walking and talking to complex decision-making.
The appeal of these robots lies in their ability to integrate into human-centric spaces. Whether it’s assisting in healthcare or providing companionship, their human-like design makes interactions more intuitive. But creating a robot that mimics human capabilities is no small feat—it requires a symphony of cutting-edge technologies.
The Technology Behind a Robot That is Like a Human
Building a robot that mirrors human functionality involves three core pillars: AI and decision-making, biomechanics, and sensory systems. Let’s break them down.
1. Artificial Intelligence: The Brain of the Robot
At the heart of every Humanoid Robot is AI, the system that enables decision-making, learning, and interaction. AI algorithms process vast amounts of data to help robots understand their environment, recognize faces, interpret speech, and respond appropriately.
Machine Learning (ML): Robots like Sophia, developed by Hanson Robotics, use ML to improve their conversational abilities over time. Sophia can analyze speech patterns and adapt her responses to sound more natural.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP allows robots to understand and generate human language, making interactions feel more lifelike.
Computer Vision: Through cameras and image recognition, robots can identify objects, people, and even emotions. For example, Atlas, created by Boston Dynamics, uses computer vision to navigate complex terrains.
2. Biomechanics: Mimicking Human Movement
Creating a robot that moves like a human is a monumental challenge. Humanoid robots rely on advanced biomechanics to replicate natural motions like walking, grasping, or even dancing.
Actuators and Motors: These are the “muscles” of the robot, enabling precise movements. Atlas, for instance, uses hydraulic actuators to perform acrobatic feats like backflips.
Skeletal Structure: A humanoid’s frame is designed to mimic human joints and limbs, allowing for flexibility and balance.
Balance and Coordination: Sensors like gyroscopes and accelerometers help robots maintain stability. Atlas uses real-time feedback to adjust its posture on uneven surfaces.
The result is a robot that can navigate human environments, from climbing stairs to picking up objects, with remarkable precision.
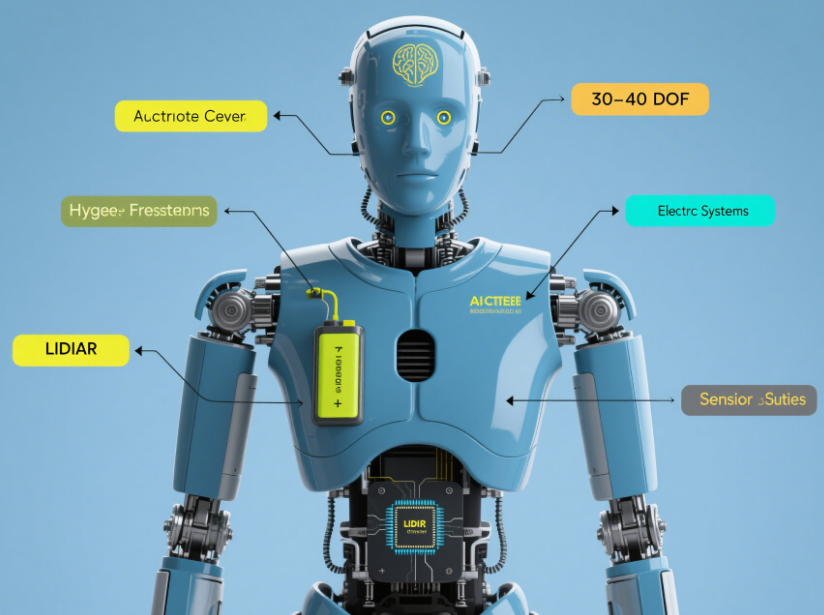
3. Sensory Systems: The Robot’s Senses
To interact with the world, humanoid robots rely on a network of sensors that act as their eyes, ears, and touch receptors.
Cameras and LIDAR: These provide visual data for navigation and object recognition.
Microphones: Used for voice recognition and environmental sound analysis.
Tactile Sensors: These allow robots to “feel” objects, ensuring delicate handling. For example, Sophia’s hands are equipped with sensors to adjust grip strength.
By integrating these systems, robots can perceive and respond to their surroundings in real time, making them more autonomous and adaptable.
Is it Possible to Make a Robot That Looks Like a Human?
Yes, it’s not only possible but already happening. Robots like Sophia have lifelike silicone skin, expressive facial features, and human-like gestures. Hanson Robotics uses advanced materials and 3D printing to create realistic appearances, while AI powers their interactive capabilities. However, achieving a perfect human replica—both in appearance and behavior—remains a challenge due to the complexity of human emotions and unpredictable behaviors.
Want to learn more about cutting-edge humanoid robots? Check out our article on Robot That is Like a Human: Meet Atlas, Sophia & the Future.
Case Studies: Atlas and Sophia
Two standout examples of humanoid robots are Atlas and Sophia, each showcasing different strengths in robotics technology.
Atlas: The Athletic Powerhouse
Developed by Boston Dynamics, Atlas is a marvel of biomechanics. Standing at 1.5 meters tall, it can run, jump, and perform parkour with astonishing agility. Its AI-driven control systems allow it to adapt to dynamic environments, making it ideal for search-and-rescue missions or industrial tasks.
Key Features: Advanced balance, real-time obstacle avoidance, and robust physical design.
Applications: Disaster response, military support, and research.
Sophia: The Social Robot
Sophia, created by Hanson Robotics, is designed for human interaction. With a face modeled after Audrey Hepburn, Sophia can hold conversations, express emotions, and even tell jokes. Her AI is built for social engagement, making her a potential companion for the elderly or a customer service assistant.
Key Features: Facial recognition, expressive movements, and conversational AI.
Applications: Healthcare, education, and public relations.
Ethical Debates Surrounding Humanoid Robots
As humanoid robots become more advanced, they raise complex ethical questions. Here are some key debates:
Job Displacement: Could robots replace human workers in industries like healthcare or retail?
Privacy Concerns: Robots equipped with cameras and microphones could inadvertently collect sensitive data.
Human-Robot Relationships: As robots become more lifelike, could they blur the lines between human and machine interactions?
Autonomy and Control: How much independence should robots have, and who is responsible for their actions?
These debates are shaping the future of robotics, as developers and policymakers work to balance innovation with societal impact.
FAQs About Humanoid Robots
1. How do Humanoid Robots learn to interact with humans?
Humanoid robots use AI, particularly machine learning and natural language processing, to analyze human behavior and adapt their responses. Over time, they improve through data-driven learning.
2. Is it Possible to Make a Robot That Looks Like a Human?
Yes, advancements in materials like silicone and AI-driven expressions allow robots like Sophia to closely resemble humans, though replicating every nuance of human appearance remains a challenge.
3. What are the main challenges in building a Robot That is Like a Human?
Key challenges include creating realistic movements, achieving emotional intelligence, ensuring safety, and addressing ethical concerns like privacy and job displacement.
4. Are Humanoid Robots safe to use in public spaces?
While robots like Atlas and Sophia are designed with safety in mind, their use in public requires strict protocols to prevent accidents and ensure ethical deployment.
Conclusion
The journey to create a Robot That is Like a Human is a remarkable blend of AI, mechanics, and ethical considerations. From the athletic prowess of Atlas to the conversational charm of Sophia, these machines are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. However, as we embrace this technology, we must navigate the ethical challenges to ensure a future where humanoid robots enhance, rather than disrupt, our lives.
Curious to explore more about the future of robotics? Visit our AI Portal for the latest insights.