In a world racing toward automation, Robot Companies stand at a critical crossroads. They promise efficiency and innovation, yet face mounting concerns over bias, job losses, and safety. Are the leaders at Robot Companies like Boston Dynamics and OpenAI truly prepared to earn public trust? This article dives into the ethical challenges and reveals whether these Robot Companies can walk the talk.
Understanding the Stakes for Robot Companies

Robot Companies design machines that think and move. Yet, 52% of consumers distrust AI decision-making, according to Pew Research in 2023. That trust gap looms large for robotics companies aiming to deploy intelligent systems in homes and factories. When a humanoid robot company launches a new model, every misstep can erode confidence.
Expert Quote: “Public trust in robotics hinges on transparency,” says Dr. Emily Hart, Ethics Lead at a leading AI Robot Companies consortium. “Companies must share their data and decision rules to break down fear of hidden biases.”
Bias in Algorithms and the Role of Robot Companies
Algorithmic bias can amplify discrimination when not checked. If a boston dynamics robot is used in security roles, any flaw in its facial recognition could lead to wrongful detention. That scenario damages the reputation of robot companies globally. To counteract bias, firms must adopt rigorous testing with diverse datasets.
OpenAI and similar autonomous robot companies now include external audits to certify fairness. Such steps are vital for maintaining credibility as AI moves from labs to the real world.
Job Displacement: A Challenge for Robot Companies
Brookings Institution projects that 30% of industrial jobs could be automated by 2030. Workers worry that industrial robot companies will replace human labor, deepening social inequality. If Robot Companies do not offer retraining programs, they risk backlash from communities and regulators.
Several delivery robot companies now partner with local job centers to reskill staff. These collaborations demonstrate how ethical foresight can soften the impact of automation.
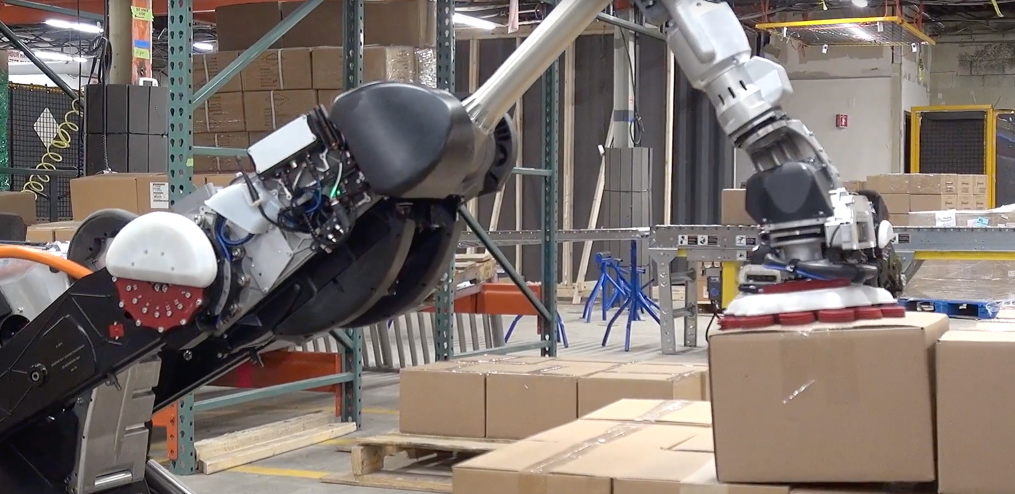
Case Study: Boston Dynamics Spot was trialed in warehouse settings to lift heavy loads. After early concerns about layoffs, the project leaders introduced a training initiative. Within six months, 80% of affected workers transitioned into new technical roles supporting the robot fleet.
Safety Protocols and Accountability at Robot Companies
Safety is non-negotiable for robot manufacturing companies. Robots must operate without endangering humans or property. Yet high‐profile incidents—like an industrial arm malfunction—highlight gaps in quality control. For public trust, Robot Companies need clear recall policies and real-time monitoring.
Leading robotic surgery companies now embed fail‐safe mechanisms and redundant sensors. These designs reduce risks and set new benchmarks for the entire industry.
Regulation and the Future of Robot Companies
Governments are drafting rules for AI and robotics. Stricter regulations could raise compliance costs but also boost consumer confidence. Robot Companies that lead with self-regulation will shape these laws and gain first‐mover advantages. Collaboration with NGOs and academic centers can further legitimize industry practices.
Point Analysis:
Transparency: Publicly share data sources and decision frameworks.
Engagement: Involve community stakeholders in deployment plans.
Accountability: Establish clear lines of responsibility for failures.
Support: Offer retraining and career-transition programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are the main ethical concerns for Robot Companies?
A1: Bias in AI, job displacement, and safety failures top the list. Companies must address each with concrete policies.
Q2: How can Robot Companies build public trust?
A2: By promoting transparency, conducting third‐party audits, and investing in community engagement and worker retraining.
Q3: Will regulations stifle innovation at Robot Companies?
A3: Thoughtful regulation can guide ethical growth. Firms that self‐regulate early will influence rulemaking and maintain innovation.
Q4: Are smaller Robot Companies at a disadvantage?
A4: Smaller firms may lack resources for audits and training programs. Partnerships and shared frameworks can help level the playing field.
Summary
The future of Robot Companies depends on their ability to tackle bias, protect jobs, and guarantee safety. Industry leaders like Boston Dynamics and OpenAI have begun making strides, but more work lies ahead. Public trust is not granted—it must be earned through transparency, accountability, and collaboration. Only then can Robot Companies unlock the full promise of ethical, responsible automation.