Imagine walking into a hospital where a robot assists surgeons with unparalleled precision, or a hotel where a robotic concierge greets you by name. This isn't science fiction—it's happening today. Service Robot Examples are proliferating across industries, transforming how we live, work, and interact. These AI-powered machines are no longer confined to factory floors; they're entering our daily lives in surprisingly sophisticated ways. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore groundbreaking real-world applications that demonstrate how service robots are solving complex problems, enhancing efficiency, and creating new possibilities across diverse sectors.
What Defines a Service Robot?
Before diving into specific Service Robot Examples, it's crucial to understand what distinguishes them from industrial robots. Unlike their manufacturing counterparts designed for repetitive tasks in controlled environments, service robots operate alongside humans in dynamic, unstructured settings. They're typically equipped with advanced sensors, machine learning capabilities, and often possess some degree of autonomy. The International Federation of Robotics categorizes service robots into professional and personal types, with applications ranging from healthcare and logistics to domestic chores and entertainment. What unites them is their fundamental purpose: to assist humans by performing useful tasks.
Groundbreaking Service Robot Examples Across Industries
1. Moxi: The Hospital Helper

Moxi is a revolutionary robot assistant that's transforming hospital operations. This socially intelligent robot features a robotic arm mounted on a mobile base, allowing it to navigate busy corridors, operate elevators, and retrieve and deliver supplies. What makes Moxi exceptional is its ability to learn hospital workflows and predict needs before they're explicitly requested. By handling time-consuming logistical tasks like fetching medications, delivering lab samples, and bringing supplies to nurses' stations, Moxi enables healthcare professionals to focus more attention on patient care. This is one of the most practical Service Robot Examples demonstrating how automation can enhance rather than replace human capabilities in critical environments.
2. Spot: The Agile Inspector
Boston Dynamics' Spot represents a paradigm shift in mobile robotics. This quadruped robot moves with remarkable agility across challenging terrain, making it ideal for inspection tasks in hazardous environments. Energy companies deploy Spot to inspect remote equipment and infrastructure, construction sites use it for progress monitoring and safety checks, and public safety agencies employ it for reconnaissance in dangerous situations. Spot can be equipped with various sensors including thermal cameras, LIDAR, and radiation detectors, collecting data that would be difficult or dangerous for humans to obtain. This example showcases how service robots can expand human capabilities in extreme environments.
3. Pepper: The Emotional Companion
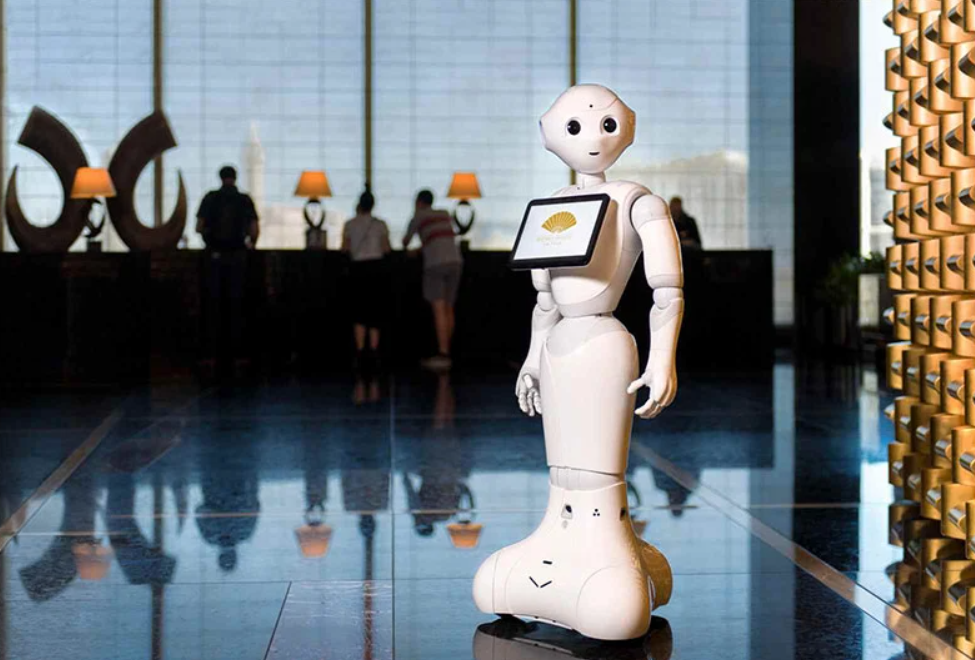

SoftBank Robotics' Pepper represents a fascinating category of social robots designed to recognize and respond to human emotions. Equipped with sophisticated emotion recognition capabilities through facial analysis and voice tone detection, Pepper can adapt its behavior accordingly. While initially deployed in retail environments as a greeter and information provider, Pepper has found perhaps its most meaningful application in healthcare settings, particularly in elder care facilities. There, it provides companionship, cognitive stimulation, and even basic reminders for medication. This emotional dimension makes Pepper one of the most human-centered Service Robot Examples available today.
4. Relay: The Hotel Courier
The hospitality industry has embraced robotics with Savioke's Relay, an autonomous delivery robot that's becoming increasingly common in hotels worldwide. Relay navigates independently through crowded lobbies, calls elevators, and delivers items directly to guest rooms. During the pandemic, its contactless delivery capability became particularly valuable. What makes Relay noteworthy is its seamless integration into existing hotel operations and its ability to interact naturally with guests through a touchscreen interface. This example demonstrates how service robots can enhance customer experiences while optimizing operational efficiency.
5. Da Vinci: The Surgical Precisionist
While technically a surgical system rather than an autonomous robot, the Da Vinci Surgical System represents a crucial category of service robots in healthcare. This sophisticated platform translates a surgeon's hand movements into smaller, precise movements of tiny instruments inside the patient's body. The system provides magnified 3D high-definition vision and allows for operations through tiny incisions, resulting in less blood loss, quicker recovery times, and reduced pain for patients. The Da Vinci system exemplifies how robotic assistance can enhance human capabilities in tasks requiring extreme precision.
6. Loomo: The Personal Transport Companion
Segway's Loomo represents an innovative approach to personal transportation and assistance. This self-balancing vehicle can transform between a rideable personal transporter and an autonomous following companion that carries belongings. Using computer vision and follow-me technology, Loomo can track and follow its owner while avoiding obstacles. This dual functionality makes it one of the most versatile personal Service Robot Examples, offering both transportation utility and assistance with carrying items in environments like airports, large campuses, or shopping centers.
7. Temi: The Personal Assistant
Temi represents a new category of personal service robots designed for home and office environments. This autonomous robot features a touchscreen interface and can navigate intelligently around spaces, responding to voice commands. Temi can make video calls, play media, provide information, and even patrol spaces remotely when the owner is away. Its advanced mapping and navigation capabilities allow it to learn environments and move between rooms autonomously. This example illustrates how service robots are becoming increasingly integrated into our personal spaces as multifunctional assistants.
8. Aethon TUG: The Logistics Expert
In healthcare logistics, the Aethon TUG robot has become an indispensable workhorse in hundreds of hospitals worldwide. These autonomous mobile robots transport medications, laboratory specimens, equipment, and supplies throughout hospital facilities. The TUG navigates using a sophisticated mapping system, calls and rides elevators independently, and can even open doors. What makes this system remarkable is its integration with hospital inventory systems, allowing it to manage and optimize material flow. This is one of the most established and proven Service Robot Examples in healthcare logistics.
9. PARO: The Therapeutic Companion
PARO is a therapeutic robot designed to look like a baby harp seal, created specifically for patients with dementia, Alzheimer's, and other cognitive disorders. Classified as a medical device by the FDA, PARO responds to touch, light, sound, temperature, and posture with movements and vocalizations. Studies have shown that interaction with PARO can reduce stress, anxiety, and the need for psychotropic medications in elderly patients. This example demonstrates how service robots can provide emotional and psychological benefits beyond practical tasks.
10. Knightscope Security Robots: The Autonomous Guardians
Knightscope's security robots represent a new approach to public safety and property protection. These autonomous machines patrol predetermined areas, detecting anomalies through cameras, thermal imaging, license plate recognition, and other sensors. They can detect unauthorized personnel, identify potential threats, and provide real-time situational awareness to security personnel. While controversial in some applications, these robots illustrate how service robotics is expanding into domains traditionally requiring human presence and judgment.
The Technology Behind Modern Service Robots
The remarkable capabilities exhibited in these Service Robot Examples are made possible by converging technological advancements. Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) algorithms enable spatial awareness and navigation. Computer vision systems allow object recognition and person detection. Natural language processing facilitates human-robot interaction. Machine learning enables adaptation to changing environments. And cloud connectivity allows for data sharing and remote operation. Understanding these underlying technologies helps appreciate the sophistication of modern service robots beyond their visible applications.
This technological evolution is part of The Service Robot Revolution: How AI-Powered Machines Are Transforming Our World, a broader movement that's reshaping industries and societal norms.
Implementation Considerations for Service Robots
Successful deployment of service robots requires careful consideration of several factors. Integration with existing workflows and systems is crucial—robots that disrupt rather than enhance processes will likely fail. Staff training and change management are equally important, as human workers need to understand how to interact with and benefit from robotic colleagues. Cost-benefit analysis must account not just for acquisition costs but also maintenance, updates, and potential workflow modifications. Ethical considerations around data privacy, job displacement, and decision-making autonomy also require careful attention when implementing these technologies.
Future Trends in Service Robotics
The Service Robot Examples we see today represent just the beginning of this technological revolution. Several trends are shaping the future landscape: increased collaboration between humans and robots (cobots), greater behavioral intelligence allowing more natural interactions, enhanced mobility capabilities for navigating complex environments, and improved learning abilities that enable robots to adapt to new tasks without explicit reprogramming. As these technologies mature, we can expect service robots to become more affordable, capable, and integrated into our daily lives across even more domains.
Frequently Asked Questions About Service Robot Examples
What distinguishes service robots from industrial robots?
Service robots primarily operate in human environments performing useful tasks for people or equipment, whereas industrial robots typically work in controlled settings performing manufacturing processes. Service robots generally have more advanced sensors, navigation capabilities, and often some level of autonomy to function in dynamic environments alongside people.
How much do service robots typically cost?
Costs vary dramatically based on capabilities and applications. Simple delivery robots might cost 10,000-30,000, while sophisticated surgical systems can exceed $2 million. Implementation costs including integration, training, and maintenance must also be considered alongside the purchase price.
Are service robots replacing human workers?
Most service robots are designed to augment rather than replace human capabilities. They typically handle repetitive, dangerous, or physically demanding tasks, allowing human workers to focus on higher-value activities requiring judgment, creativity, and emotional intelligence. In many cases, service robots create new types of jobs while transforming existing roles.
What are the main challenges in deploying service robots?
Key challenges include navigating unstructured environments reliably, integrating with existing systems and workflows, ensuring safety around humans, managing costs, addressing privacy concerns, and achieving social acceptance. Technical limitations in understanding context and adapting to unexpected situations also present significant hurdles.
Conclusion: The Service Robot Landscape
The diverse Service Robot Examples explored in this article demonstrate how robotics technology is moving beyond manufacturing into virtually every aspect of our lives. From healthcare to hospitality, these machines are enhancing human capabilities, improving efficiency, and performing tasks that would be dangerous, tedious, or impossible for people alone. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated applications to emerge, fundamentally transforming how services are delivered and experienced. The key to successful implementation lies in focusing on collaboration between humans and machines, ensuring that robotic systems enhance rather than replace the human touch that remains essential in service contexts.